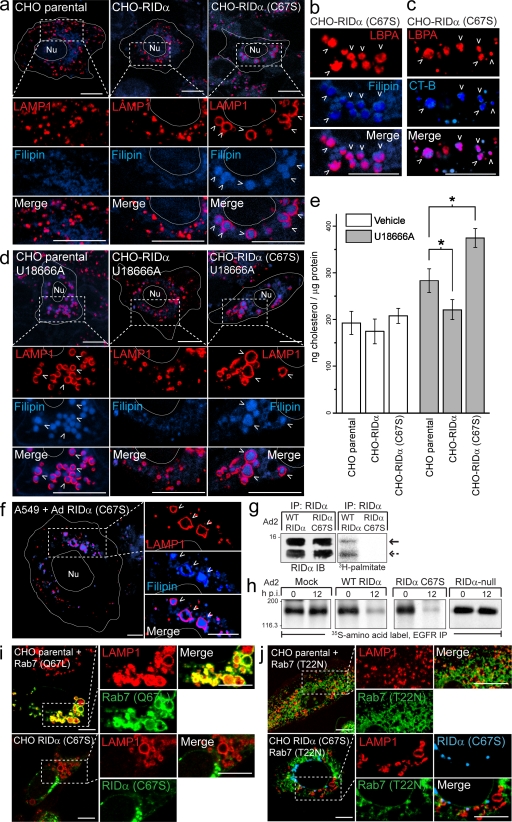
Figure 4.
RID-α (C67S) induces the formation of enlarged lipid-filled LAMP1 structures. (a) Confocal images of CHO cell lines stained with LAMP1 antibody and filipin. (b and c) Magnified images of single and merged channels from CHO–RID-α (C67S) cells stained with LBPA antibody and filipin (b) or LBPA antibody after incubation with Alexa Fluor 647 CT-B (c). (d) CHO cell lines treated with U18666A for 8 h and stained with LAMP1 antibody and filipin. (e) Cholesterol quantification in CHO cell lines treated with DMSO (vehicle) or U18666A for 8 h using the Amplex red cholesterol assay kit. Values were normalized to total cellular protein and are displayed as mean ± SEM (*, P < 0.01). (f) Confocal images of A549 cells infected with a mutant RID-α (C67S) Ad2 virus and stained with LAMP1 antibody and filipin 24 h postinfection. (g) A549 cells infected with wild-type (WT) or RID-α (C67S) Ad2 viruses radiolabeled with [3H]palmitate and RID-α immunocomplexes separated by SDS-PAGE for fluorography. Arrows denote 13.7 (solid)- or 11.3 (dashed)-kD RID-α species. (h) A549 cells radiolabeled with 35S-Express Protein Labeling mix and mock infected or infected with wild-type or mutant Ad viruses and EGFR immunocomplexes analyzed by SDS-PAGE and fluorography at the times indicated. (g and h) Molecular mass is indicated in kilodaltons. (i) Parental CHO cells transfected with constitutively active (Q67L) EGFP-Rab7 and stained for LAMP1 or CHO–RID-α (C67S) cells stained for LAMP1 and RID-α. (j) Parental CHO or CHO–RID-α (C67S) cells transfected with dominant-negative (T22N) EGFP-Rab7 and stained for LAMP1 (parental) or LAMP1 and RID-α (CHO–RID-α (C67S)). (a–d and f) Arrowheads indicate examples of costained vesicles. (a, d, f, i, and j) Boxed areas show regions of the image that were magnified. (a, d, and f) Cell and nucleus (Nu) boundaries were drawn using MetaMorph software. IB, immunoblot; IP, immunoprecipitation; p.i., postinfection. Bars, 10 µm.