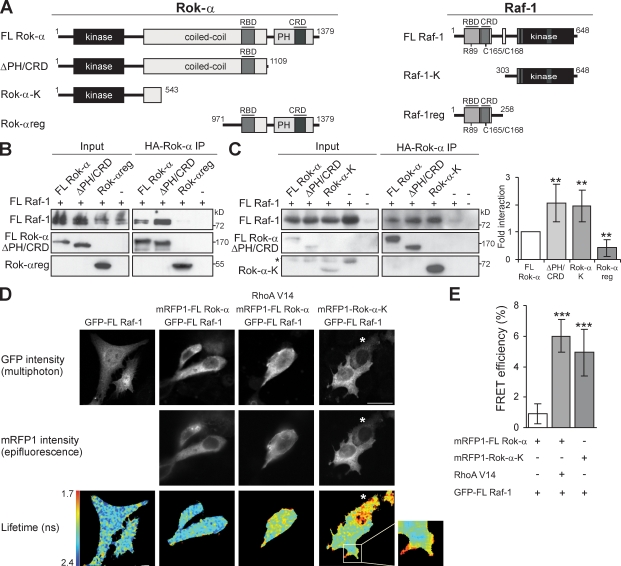
Figure 1.
Raf-1 interacts with the Rok-α kinase domain. (A) Rok-α and Raf-1 proteins used in this study are shown. The phosphorylation and Ras-binding site mutants are indicated. (B and C) HA-tagged Rok-α was immunoprecipitated from COS-1 cells cotransfected with Rok-α and FL Raf-1. Input (1.5%) and the immunoprecipitates (IP) were immunoblotted with Raf-1, HA (B), or Rok-α (C) antibodies. *, unspecified band. The amount of Raf-1 coprecipitating with the Rok-α mutant proteins is plotted as fold of FL Raf-1–Rok-α interaction (set as 1; mean ± SD of four experiments). (D) Fluorescence lifetime (τ), GFP intensity, and mRFP1 intensity in MCF-7 cells transfected with the indicated constructs. RhoAV14 expression was verified by staining with Flag antibody. The cell marked with the asterisks was excluded from the cumulative FRET efficiency analysis in E because of insufficient photon counts (see Material and methods). Inset shows a magnified view of the boxed region. (E) Percentage of FRET efficiency (mean ± SD of three experiments) is shown. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.005. Bars, 20 µm.