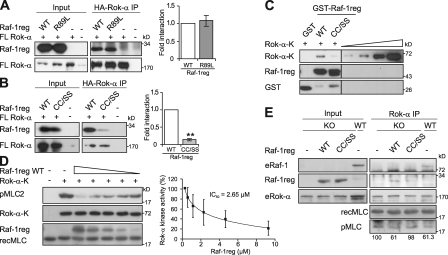
Figure 3.
Raf-1reg interacts with Rok-α and inhibits its kinase activity. (A and B) CRD but not RBD mutation disrupts the binding of Raf-1reg to Rok-α. HA immunoprecipitates (IP) were analyzed as in Fig. 1. The mean ± SD of at least three experiments is shown. **, P < 0.01. (C) Rok-α–K interacts in vitro with Raf-1reg WT but not with Raf-1reg CC/SS. 2 µg GST, GST–Raf-1reg WT, or GST–Raf-1reg CC/SS on glutathione Sepharose beads were incubated with 25 ng His-tagged Rok-α–K. Rok-α–K and GST proteins were detected by immunoblotting with His and GST antibody. 3.125–25 ng recombinant Rok-α–K was loaded as a reference on the same gel. One representative experiment out of three is shown. Black lines indicate that intervening lanes have been spliced out. (D) Dose-dependent inhibition of Rok-α–K by purified Raf-1reg. 0.29–9.3 µM Raf-1reg was incubated with 100 ng Rok-α–K (0.05 µM) before a Rok kinase assay with 7 µM recombinant MLC2 (recMLC2) as a substrate. The mean ± SD of three experiments is shown. (E) Raf-1reg inhibits Rok-α activity in vivo. The activity of endogenous Rok-α (eRok-α), immunoprecipitated from WT and KO MEFs, and from KO MEFs transfected with Raf-1reg WT or Raf-1reg CC/SS was assessed as in D. Rok-α activity, expressed as pMLC/MLC ratio and normalized by the amount of Rok-α present in the assay, is indicated below each lane. Rok-α activity of Raf-1 KO MEFs is set to 100%.