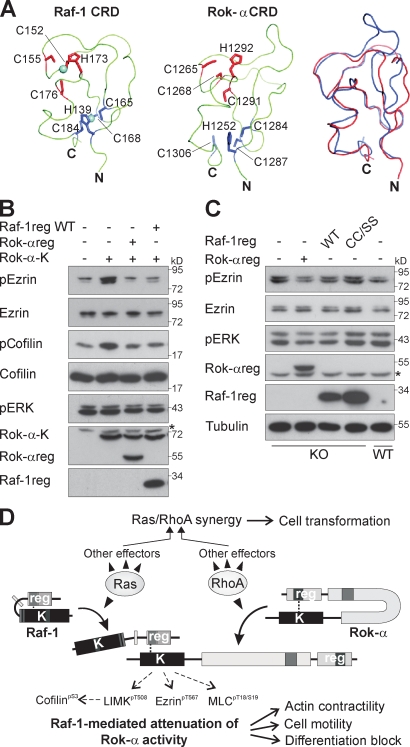
Figure 5.
The regulatory domains of Raf-1 and Rok-α act as inhibitors of Rok-α kinase activity in vivo. (A) Comparison of the experimental solution structure of Raf-1 CRD (left) and the computational model of the Rok-α CRD (middle). Zinc cations are shown as spheres, and the side chains of the residues coordinating the cations are shown as lines: red in one metal biosite and blue in the other. (right) Superposition of the Raf-1 and Rok-α CRDs. (B and C) COS-1 cells (B) and MEFs (C) were transfected with the indicated constructs. 24 h after transfection, cells were lysed and analyzed by immunoblotting. KO, Raf-1 KO MEFs; *, unspecific band. (D) Model of the regulation of Rok-α by Raf-1. GTPase binding disrupts intramolecular interaction between the regulatory and kinase domains of Raf-1 and Rok-α, upon which Raf-1reg binds to the kinase domain of Rok-α, restraining Rho-induced Rok-α kinase activity. Inhibition in trans limits the phosphorylation of Rok-α downstream targets, regulating cell motility and differentiation.