Fig. 4.
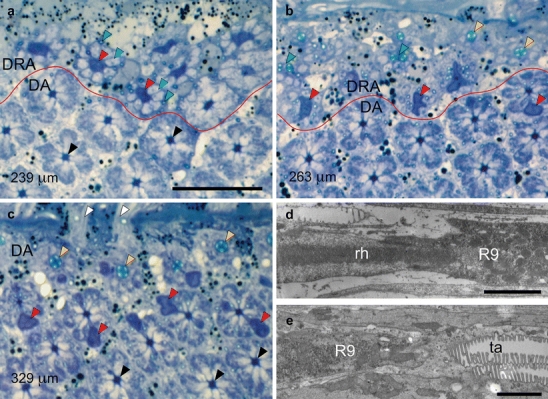
a–c Position of proximal retinula cell R9 with respect to rhabdom and tapetum in the ommatidia of the dorsal rim area (DRA) and unspecialized dorsal area (DA) of the compound eye. Light micrographs of tangential sections through the dorsalmost part of an eye at progressively deeper proximal levels of the retina. Specifications in micrometers (bottom left) indicate section levels relative to cornea surface. R9 cells can be recognized by their dark blue stain (red lines border between DRA and unspecialized DA). Bar 20 μm a Section plane just proximal to the end of the rhabdoms in the DRA. R9 cells (red arrowheads, large dark profiles) in the DRA are surrounded by the axons of V, H, and D cells (blue arrowheads, large light profiles) and tracheoles (green arrowheads, small profiles), replacing the rhabdoms. In the longer DA ommatidia, V, H, and D cells still form rhabdoms at this level (black arrowheads). b Section plane near the junction between R9 cells and tapeta in the DRA. DRA ommatidia exhibit either R9 (red arrowheads, large dark profiles), tapeta (yellow arrowheads), or tracheoles in the process of fusing (green arrowheads). In one of the DA retinulae, the proximal end of the rhabdom is indicated by the presence of an eccentric R9 (red arrowhead). c Section plane near the junction between rhabdoms and tapeta in the DA. At this level, the axons of the DRA ommatidia have left the retina, and only DA retinulae are visible. Since ommatidial length increases with distance from the eye rim, this section shows DA ommatidia at three levels: (1) V, H, and D cells form the rhabdoms (black arrowheads), (2) H, D, and the bilobed R9 cells (red arrowheads, dark profiles) form the rhabdoms, and (3) tapeta (yellow arrowheads). Retinula cell axons (white arrowheads) penetrate the basement membrane. d, e Position of R9 with respect to rhabdom and tapetum in the ommatidia of the DRA. Electron micrographs of longitudinal sections in the proximal part of the retina (left distal). Bars 2 μm d The elongated microvilli-less cell R9 begins at the proximal end of the rhabdom (rh). e The reflecting tapetum (ta) begins at the proximal end of R9. The proximal end of the rhabdom is immediately followed by the tapetum in the DA, whereas R9 sits between the rhabdom and the tapetum in the DRA
