Fig. (2).
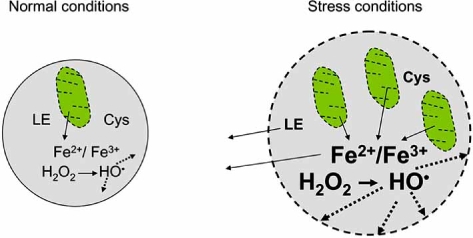
Tentative mechanism of lysosomal membrane permeabilization secondary to enhanced reparative autophagy. Reparative autophagy is induced by cellular damage under stress conditions. It is associated with increased number and size of lysosomes (autolysosomes) containing mitochondria and other damaged cellular structures under degradation. This may result in the release of redox-active iron from mitochondrial metalloproteins, activation of Fenton reactions and generation of hydroxyl radicals with ensuing damage to the lysosomal membrane (shown as dashed line). See detailed explanations in the text.
