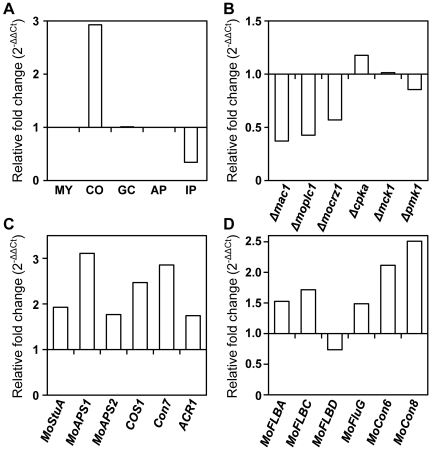
Figure 4. Transcriptional expression patterns of MoHOX2 and conidiogenesis-related genes.
(A) Expression of MoHOX2 during M. oryzae development. The tissues examined were submerged mycelia (MY), purified conidia (CO), germinated conidia (GC), appressoria (AP), and infected plants (IP). Measurements of MoHOX2 transcripts obtained by quantitative RT-PCR analysis were normalized to β-tubulin and expressed as relative values, with 1 corresponding to the MY. See Materials and Methods for details. (B) Expression of MoHOX2 in various deletion mutants. These include Δmac1, Δmoplc1, Δmocrz1, Δcpka1, Δmck1, and Δpmk1, and their genotypes were described in Table 1. The abundance of MoHOX2 transcripts in a mutant is expressed relative to a value of 1 in the wild-type KJ201. RNAs of the mutants were extracted from mycelia grown in CM liquid medium for 4 days. (C) Expression of conidiogenesis-related M. oryzae genes. The abundance of conidiogenesis-related transcripts in ΔMohox2 is expressed as a relative value, with 1 corresponding to MoHOX2 transcripts in the wild-type. (D) Expression of M. oryzae genes homologous to known conidiogenesis-related genes in other fungi. The abundance of conidiogenesis-related transcripts in ΔMohox2 is expressed as a relative value, with 1 corresponding to the level of MoHOX2 transcripts in the wild-type.