Figure 2. Close-up view of CacOgg residues interacting with 8-oxoG.
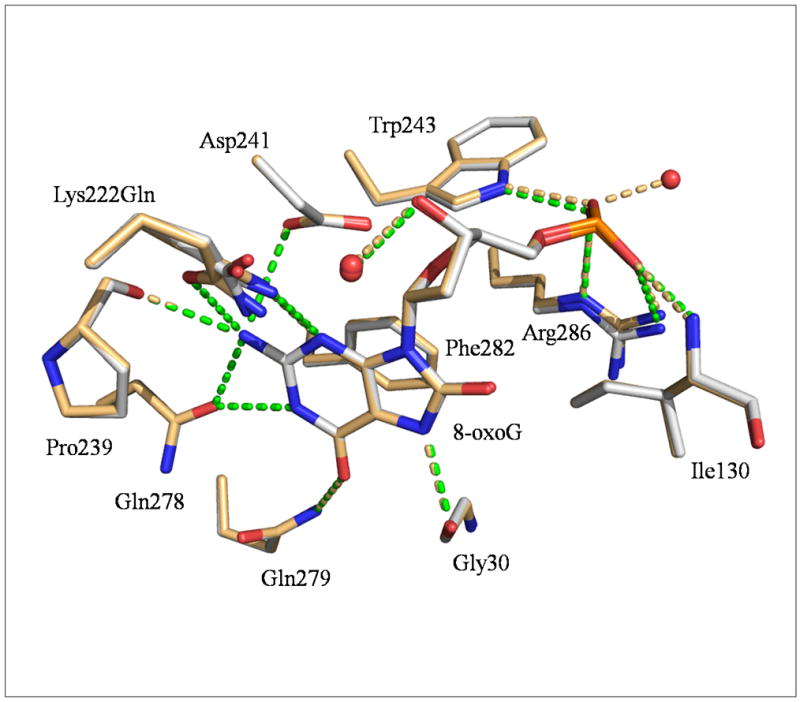
CacOggK222Q/8-oxoG:C and/8-oxoG:A are superimposed. Only residues involved in H-bonds and stacking interactions with 8-oxoG are depicted. The CacOggK222Q/8-oxoG:C carbon atoms are shown in light grey and those of the 8-oxoG:A complex in light orange. Gln222 appears to adopt alternate conformations in both complexes. H-bonds are represented by green dashed lines for 8-oxoG:C complex and light orange dash line for 8-oxoG:A complex. The H-bond between 8-oxoG N7 H atom and the main chain carbonyl of Gly30 has been shown to be essential for the recognition of 8-oxoG in hOGG1[26, 39].
