Figure 1.
Expression of Fz4 in ECs and Ndp in Muller glia: absence of Fz4 signaling in ECs leads to severe defects in retinal vascular development.
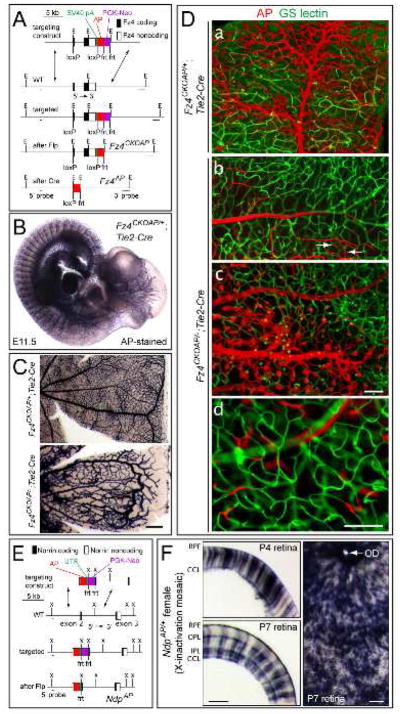
(A) Structure of the Fz4CKOAP allele. LoxP sites were placed in the 5′ UTR and 3′ of the 3′ UTR. Cre-mediated recombination deletes Fz4 coding sequences and activates AP. E, EcoR I.
(B) Fz4 is expressed in ECs as determined by AP histochemistry of a Fz4CKOAP/+;Tie2-Cre E11.5 embryo.
(C) AP histochemistry of adult retinas. Fz4AP/+ ECs produce a WT vasculature, and Fz4AP/− ECs produce a vascular phenotype identical to that of Fz4−/− mice. Scale bar, 200 um.
(D) Mosaic analysis of Fz4CKOAP/+;Tie2-Cre and Fz4CKOAP/−;Tie2-Cre retinas with incomplete Cre-mediated recombination. a, Fz4AP/+ ECs populate large vessels and capillaries. b–d, vessels are populated by Fz4AP/− ECs only if they reside on the vitreal surface (b and c); intraretinal growth of Fz4AP/− ECs typically ends in a compact ball of cells (c), with some Fz4AP/− ECs incorporated into the adjacent WT capillary network (white arrows in b). d, rare Tie2-Cre-mediated recombination events generate isolated Fz4AP/− ECs within mature intra-retinal capillaries. Scale bar, 100 um.
(E) Structure of the NdpAP allele. UTR, rabbit beta-globin 3′ UTR; X, Xba I.
(F) AP-stained retinas from NdpAP/+ female mice. 40 um cross-sections at P4 and P7 (left) and a flat mount at P7 (right). AP+ Muller glia span the full thickness of the retina. The brown dots in the flat mount are adherent RPE cells. Scale bars, 100 um. RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; OPL, outer plexiform layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer, GCL, ganglion cell layer; OD, optic disc.