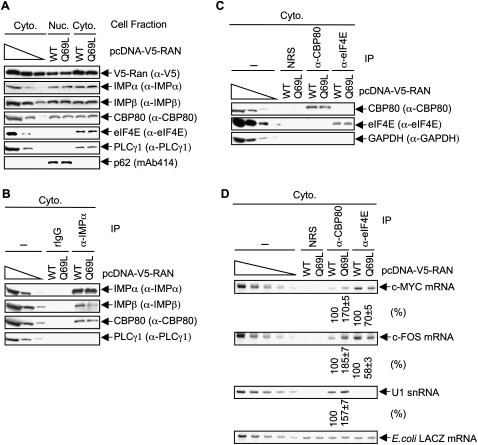
Figure 7.
Inhibiting the interaction of IMPα with IMPβ by expressing RAN(Q69L) augments the co-IP of CBP80 with c-MYC, c-FOS, IRE-Gl mRNAs, and U1 snRNA, and concomitantly decreases the co-IP of eIF4E with c-MYC and c-FOS mRNAs. (A) HeLa cells (1 × 107) were transiently transfected with pcDNA-RAN(WT) or pcDNA-RAN(Q69L) (30 μg). Nuclear and cytoplasmic lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis using the specified antibody (α). The distributions of p62 and PLCγ1 demonstrate that cellular fractions are free of detectable cross-contamination. (B) As in Figure 6B, except PLCγ1 was used to control for IP specificity. (C) As in Figure 6C. (D) As in Figure 6D, except IRE-Gl mRNA was not measured. Notably, it has been shown that RANQ69L expression, like IBB expression (Fig. 6), does not alter the cytoplasmic level of mRNA (Clouse et al. 2001). Results are representative of two independently performed experiments.