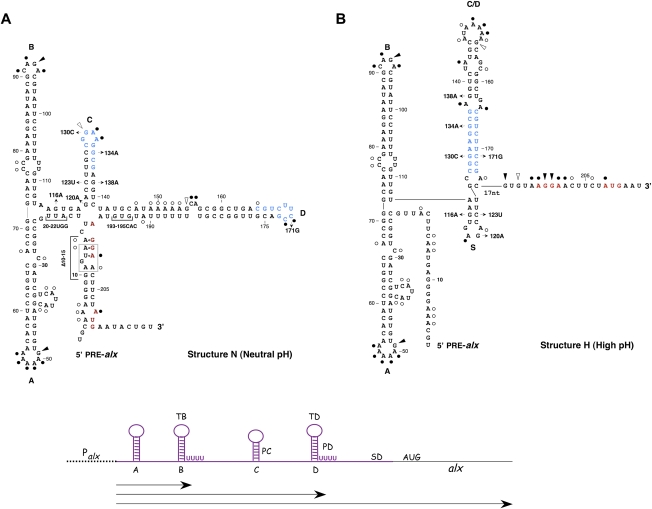
Figure 1.
Proposed PRE-alx RNA conformations. Primary (A) and alternative (B) structures predicted to form under neutral pH (structure N) and high pH (structure H) conditions, respectively. The Shine-Dalgarno and the initiation codon of alx are in red. Complementary sequences in hairpins C and D are in blue. Arrows indicate specific nucleotide changes generated randomly or by site-directed mutagenesis. Brackets indicate multiple mutations or deletions. To form structure H, the lower part of hairpin C folds into the small hairpin S, while base-pairing between loops C and D forms hairpin C/D. The loop E motif in structure N is boxed (dashed line). The probing data obtained with the G116A mutant are displayed on structure N (A), while G134A data are shown on structure H (B). Circles indicate strong (filled circles) and weak (open circles) DMS modification sites. Triangles indicate strong (filled) and weak (open) nuclease T1 cleavage sites. A schematic representation of the genetic elements of PRE-alx RNA is shown at the bottom of the figure. Indicated are the promoter of alx (Palx); four hairpins of structure N, including two rho-independent transcription terminators at hairpins B and D (TB and TD, respectively); the Shine Dalgarno (SD); and the initiation codon of alx. Pausing sites identified and mapped in this study are indicated as PC and PD. The PRE region is in purple. A subset of PRE-alx transcripts terminates at the transcription termination signals at hairpins B and D (see also Supplemental Fig. S8). Arrows indicate stable RNA species. The two shorter species represent the previously characterized SraF.