Figure 2.
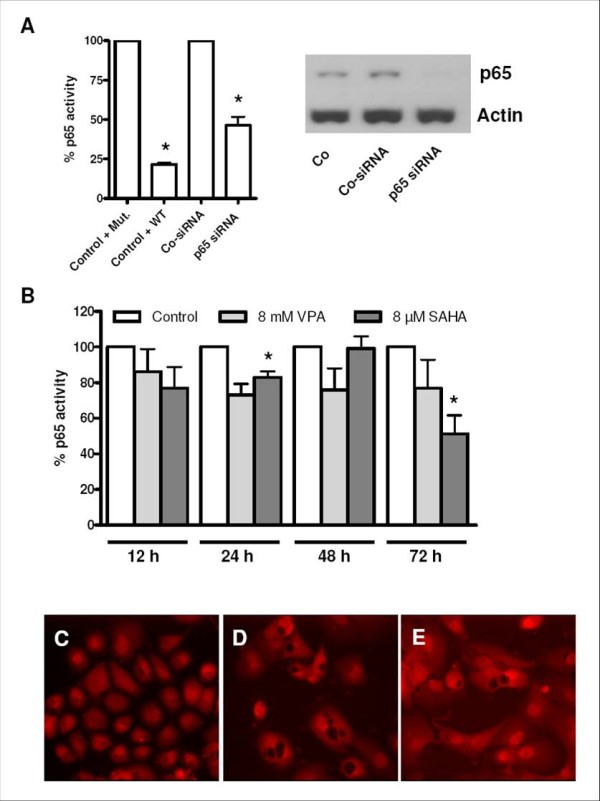
Effects of HDIs on DNA binding activity and nuclear translocation of RelA/p65 in stimulated PANC-1 cells. (A) Signal specificity of the transcription factor assay was ensured by the use of Wild Type NF-κB Competitor Duplex (WT) (normalized to Mutant NF-κB Competitor Duplex (Mut.)) as well as by specific RelA/p65 siRNA treatment (72 h, normalized to Control siRNA) (*: p = 0.05; columnar t-test); Western Blot showing specific knockdown of RelA/p65 protein expression by RelA/p65 siRNA treatment in comparison with control siRNA and untreated cells. (B) RelA/p65 binding activity as measured in a transcription factor assay was markedly diminished in response to 72 h of HDI treatment (*: p = 0.05; columnar t-test, IL-1β stimulated PANC-1 cells). (C-E) RelA/p65 specific immunofluorescence. RelA/p65 specific immunofluorescence showed a strong nuclear RelA/p65 staining in response to IL-1β stimulation (C). IL-1β induced nuclear translocation of RelA/p65 was markedly diminished by (D) SAHA treatment (8 μM) and (E) VPA treatment (8 mM) (72 h).
