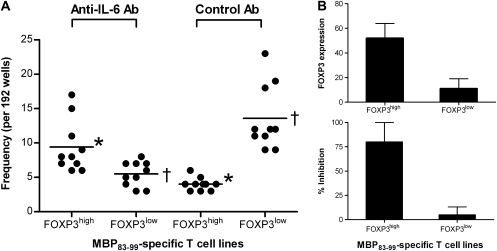
Fig. 7.
The role of IL-6 in the generation of MBP83–99-specific T cells in MS patients. (A) PBMCs isolated from MS patients (n = 10) were stimulated with MBP83–99 peptide in the presence and absence of 5 μg ml−1 anti-IL-6 antibody in 96-well plates for 7 days. Fresh antibody was supplied every other day with medium change. Cells were then tested for their specificity to MBP83–99 peptide in a proliferation assay. MBP-specific T-cell lines were selected and assayed for the expression of FOXP3 by FACS and the inhibitory function. Frequencies of MBP-specific T-cell lines expressing high or low levels of FOXP3 were calculated as number of wells of interest per total wells tested (n = 192). The statistical difference of frequencies between cell line groups was analyzed by the Student’s t-test. Asterisks (P = 0.004) and daggers (P = 0.001) indicate the comparable cell line groups with significant differences, respectively. (B) Average levels of FOXP3 in MBP83–99-specific T-cell lines (94 for FOXP3high, 55 for FOXP3low) generated in the presence of anti-IL-6 antibody from 10 MS patients were analyzed by flow cytometry. Inhibitory functions of these resultant MBP83–99-specific T-cell lines were examined by the proliferation assay using autologous CD4+CD25− T cells as responder as described in the Methods.