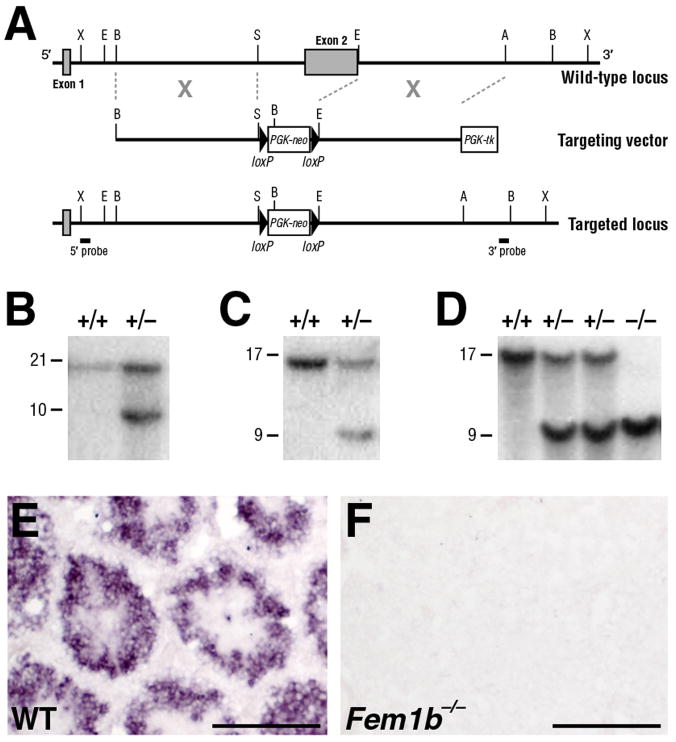
Figure 3.
Targeting of the Fem1b locus. A: Schematic depiction of the targeting strategy. The mouse Fem1b genomic locus comprises two exons (shaded boxes), with most of the coding region (aa 83 – 628) in the second exon. Homologous recombination with the targeting vector deletes the second exon, which includes most of the ankyrin repeats. The positions of the 5′- and 3′- flanking probes used for Southern blot analysis are shown. B: Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA from ES cell clones using the 5′-flanking probe, which detects a 21 kb XbaI wild-type fragment and a 10 kb fragment from the targeted allele. C: Southern blot analysis of ES cell clones using the 3′-flanking probe, which detects a 17 kb BamHI wild-type fragment and a 9 kb fragment from the targeted allele. D: Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA from wild-type, heterozygous and homozygous adult mice using the 3′-flanking probe. F, G: Section in situ hybridization analysis shows that Fem1b expression is detected at 14 weeks of age in wild-type testis (F), but not in the Fem1b homozygous testis (G). Scale bars in F, G correspond to 100 microns.