Fig. 2.
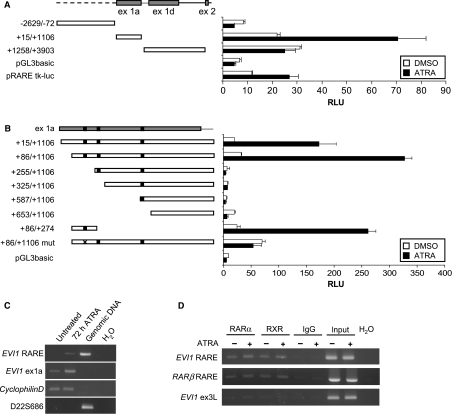
A functional RARE is located in exon 1a of the human EVI1 gene. (A) Schematic of the genomic region at the 5′-end of the human EVI1 gene and of the fragments cloned into pGL3basic, and luciferase reporter assays. Stippled line, EVI1 upstream region; grey boxes, exons (exons 1b and 1c are too small to be depicted in this schematic); solid lines, introns. The positions of cloned fragments are indicated relative to the transcriptional start site of EVI1_1a (GenBank accession no. BX640908). pRARE-tk-luc contains two copies of the human RARβ RARE and the tk minimal promoter in pGL2, and was used as a positive control for the ATRA response. For luciferase assays, the indicated reporter plasmids were transfected into NTERA-2 cells, together with the renilla luciferase plasmid pRL; 10 μm ATRA or an equivalent amount of dimethylsulfoxide was added 1 day after transfection. Another ∼ 24 h later, cells were lysed and luciferase activities were measured. Relative luciferase units (RLU) were derived by normalizing firefly to renilla luciferase activities. Error bars represent the standard deviations between duplicate measurements. White bars, dimethylsulfoxide; black bars, ATRA. (B) Schematic of EVI1(+15/+1106)/pGL3 and its derivative constructs, and luciferase reporter assays. Grey box, exon 1a; black boxes, predicted RAREs. In EVI1(+86/+1106)mut/pGL3, the six nucelotides comprising the second half-site of the EVI1 RARE were mutated (indicated by a cross). Luciferase reporter gene assays were performed as in (A). (C) RT-PCR confirming that the RARE of the EVI1 gene is located within its transcribed region. NTERA-2 cells were incubated with ATRA for 0 or 72 h. RNA was extracted, treated with DNaseI, reverse transcribed and amplified using primers flanking the EVI1 RARE (EVI1_RARE-F, EVI1_RARE-R; Table S1B), an intron-spanning primer pair located in a more proximal region of EVI1_1a (EVI1_1a-fwd, EVI1_1a-rev; Table S1A) and a primer pair for the housekeeping gene cyclophilinD (cycD-F, cycD-R; Table S1A). The effectiveness of the DNaseI treatment was verified with primers for the microsatellite marker D22S686 (D22S686-F, D22S686-R; Table S1B). (D) ChIP was performed on NTERA-2 cells treated with ATRA or dimethylsulfoxide for 24 h using an antibody specific to RARα, a pan-RXR antibody, or unspecific rabbit IgG as a negative control. Immunoprecipitated chromatin and input DNA as a positive control were amplified with primers flanking the EVI1 RARE (EVI1_RARE-F, EVI1_RARE-R; Table S1B), primers for the RARβ RARE (RARβ_RARE-F, RARβ_RARE-R; Table S1B) or with negative control primers located in EVI1 exon 3L (EVI1_ex3L-F; EVI1_ex3L-R; Table S1B).