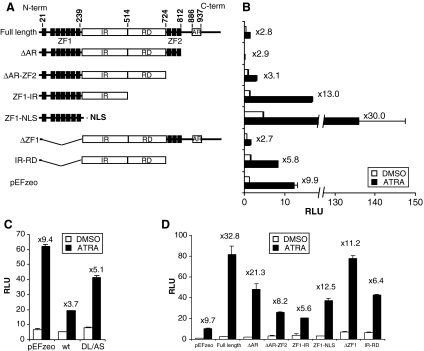
Fig. 4.
Protein domains involved in negative and positive modulation of the ATRA response by EVI1. (A) Schematic of the EVI1 deletion constructs. Black boxes, zinc finger motifs; ZF1, ZF2, zinc finger domains 1 and 2, respectively; IR, intervening region; RD, repression domain; AR, acidic region. Amino acid positions delimiting these domains are indicated. All constructs are based on the pEFzeo vector backbone, and contain an N-terminal HA epitope tag. The SV40 large T antigen NLS was engineered onto the ZF1 construct; all other constructs include a predicted NLS contained in the IR. (B–D) Luciferase assays using the indicated EVI1 deletion constructs along with the reporter vectors EVI1(+86/+1106)/pGL3 (B, C) or pRARE-tk-luc (D) were performed as described in Fig. 3. wt, wild-type EVI1; DL/AS, CtBP binding site mutant. White bars, dimethylsulfoxide; black bars, ATRA. Fold induction by ATRA in the presence of each construct is indicated. The effects of all mutations were highly reproducible; only deletion of the AR diminished the activity of EVI1 on pRARE-tk-luc more modestly in an independent experiment.