Figure 4. Notch1 Signaling Promotes the Maturation of CD4+ and CD8+ SP Thymocytes in the Absence of MHC Expression on Thymic Epithelial Cells.
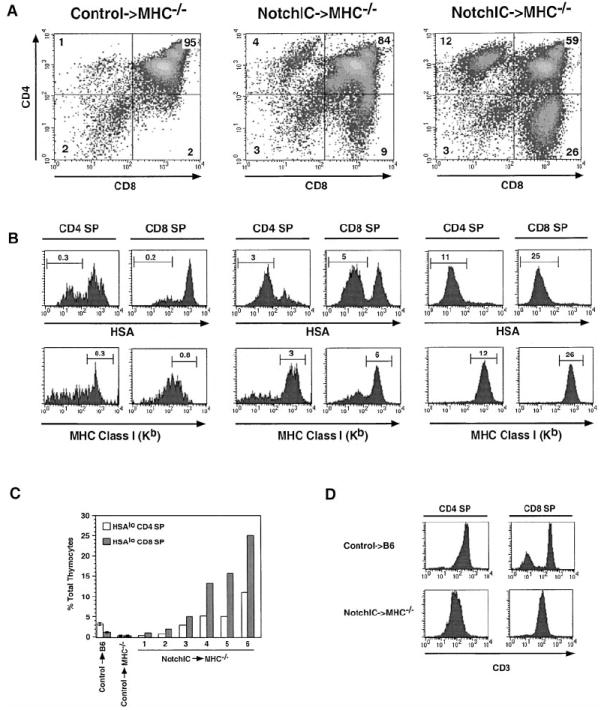
(A) FACS analysis of CD4 and CD8 expression on thymocytes from one littermate control→MHC−/− and two NotchIC→MHC−/− bone marrow chimeric mice. Numbers indicate the percent of total thymocytes that fall within the indicated quadrants.
(B) FACS analysis of HSA and MHC class I expression on CD4+ and CD8+ SP thymocytes from control→MHC−/− and NotchIC→MHC−/− bone marrow chimeric mice. CD4+ SP and CD8+ SP thymocytes from the mice shown in (A) were analyzed by FACS for expression of HSA and MHC class I. Numbers above the bars represent the percent of total thymocytes that fall within the indicated gate.
(C) Percent of HSAlo CD4+ SP and HSAlo CD8+ SP thymocytes in NotchIC→MHC−/− chimeric mice. CD4+ SP and CD8+ SP thymocytes from six NotchIC→MHC−/− chimeric mice, two littermate control→MHC−/−, and two littermate control→B6 chimeric mice were analyzed by FACS for HSA expression as in (B). The percent of HSAlo CD4+ SP and HSAlo CD8+ SP thymocytes for the NotchIC→MHC−/− chimeras mice are graphed individually. The average values for the littermate control→MHC−/− and littermate control→B6 chimeric mice are shown for reference.
(D) FACS analysis of CD3 expression on CD4+ and CD8+ SP thymocytes from NotchIC→MHC−/− and littermate control→B6 bone marrow chimeric mice.
