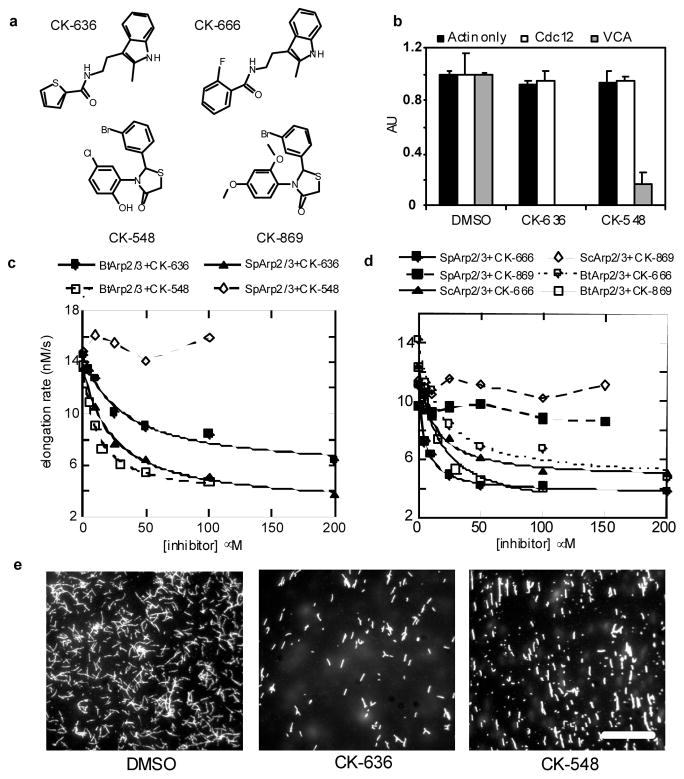
Figure 1.
Two classes of small molecules inhibit nucleation of actin filaments by Arp2/3 complex. a, Structures of CK-636, CK-548, CK-666 and CK-869. b, Inhibition of HsArp2/3 complex by CK-636 and CK-548. The time course of actin polymerization was monitored by the fluorescence increase of pyrenyl-actin. Conditions: 20 μM compound or DMSO, 2.5 μM 15% pyrenyl-actin alone or with 100 nM Cdc12(FH2) or 6 nM HsArp2/3 complex and 300 nM WASp-VCAThe maximum polymerization rate is expressed in arbitrary units. Error bars, s.d., n=4) c, Inhibition of Bos taurus (Bt) and Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Sp) Arp2/3 complexes by CK-636 and CK-548. The time course of polymerization was measured as in (1b). Conditions: 4 μM 15% pyrenyl-actin, 5 nM SpArp2/3 complex, and 1 μM N-WASp-VCA, or 3 μM 30% pyrenyl-actin, 5 nM BtArp2/3 complex and 1 μM N-WASp-VCA. CK548 was insoluble at 200 μM under the conditions used for this assay. The maximum polymerization rate of actin alone under these conditions was 4.6 nM/s. d, Effect of CK-666 and CK-869 on the polymerization of actin with bovine and yeast Arp2/3 complexes. Conditions as in 1(c) with either 3 μM 30% pyrenyl-actin and 5 nM BtArp2/3 complex or 4 μM 20% pyrenyl-actin plus 20 nM SpArp2/3 complex or 5 nM ScArp2/3 complex. Both compounds reduced the maximum polymerization rate of samples with BtArp2/3 complex to the basal rate without Arp2/3 complex but CK869 did not inhibit either yeast Arp2/3 complex. e, Fluorescence micrographs of the products of actin polymerization assays stained with Alexa 488-phalloidin. Actin (3.6 μM) was polymerized with 6 nM HsArp2/3 complex, 100 nM WASp-105-502, 300 nM Cdc42 and 100 μM CK-636 Scale bar = 20 μm.