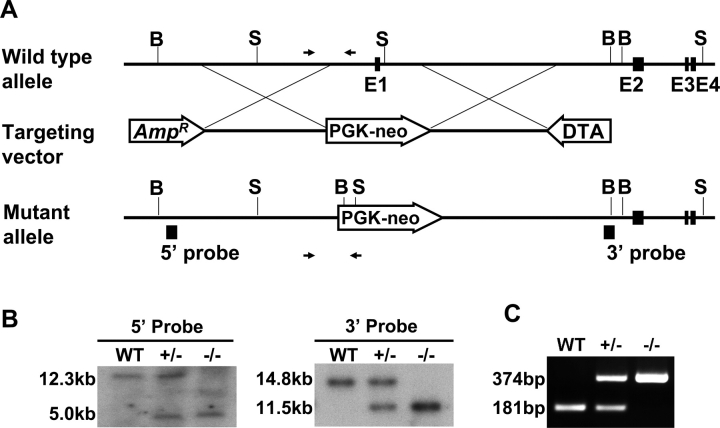
FIG. 1.
Sohlh2-knockout strategy. A) The targeting vector was designed to delete exon 1 encoding the ATG site and nucleotides upstream of exon 1. For positive and negative selections, PGK-neo (PL-452) and pDTA.3 (DTA) cassettes were used. Genomic regions amplified by PCR for genotyping are indicated by arrows. B) Southern blot analysis of tail DNA extracted from WT, Sohlh2+/–, and Sohlh2–/– mice. We used two external probes to distinguish the Sohlh2 WT alleles (12.3 kb for the 5′ probe and 14.8 kb for the 3′ probe) and null alleles (5.0 kb for the 5′ probe and 11.5 kb for the 3′ probe). Genomic DNA was isolated from mouse tails, digested with BmtI (for the 5′ probe) and SpeI (for the 3′ probe), and then hybridized to 32P-labeled 5′ and 3′ DNA probes. C) The PCR analysis for genotyping of WT, Sohlh2+/–, and Sohlh2–/– mice. The sizes of predicted WT and mutant allele amplification products are 181 bp and 374 bp, respectively.