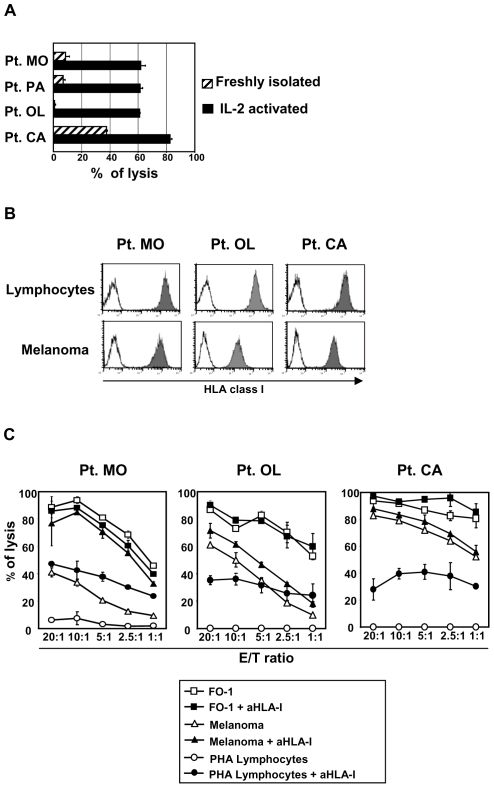
Figure 1. Cytolitic capabilities of human NK cells against autologous melanoma.
A: Susceptibility of melanoma cells to autologous NK cell-mediated lysis. Freshly isolated or IL-2 activated NK cells were used as effector cells in a specific 51chromium release assay. The effector/target (E/T) ratio used was 20∶1. Four representative patients are shown and results are expressed as means±SD derived from experiments in triplicate. B: Flow cytometry evaluation of total HLA class I expression (W6/32 mAb) on melanoma cells and, as a comparison, on autologous lymphocytes. C: Susceptibility to NK-mediated lysis of melanoma cells compared with susceptibility of HLA class I-deficient FO-1 cell line and autologous lymphocytes stimulated with PHA (PHA lymphocytes). Cytolitic activity was assessed by 51chromium release tests. In order to evaluate the inhibitory effect caused by melanoma HLA class I expression on NK cell activity, lysis of FO-1, autologous melanoma cells and PHA lymphocytes was also analysed in the presence of the anti-pan HLA class I blocking mAb (A6-136, IgM) at the indicated E/T ratios. At least three experiments were performed for each patients. Representative experiments of three patients out of six are shown. Data represent mean value±SD of experiments performed in triplicate.