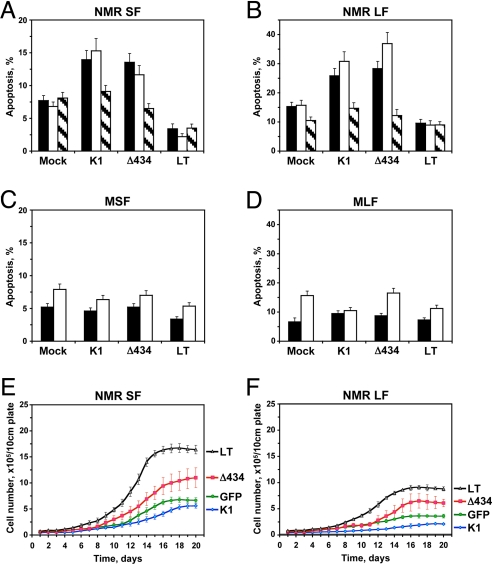
Fig. 5.
Analysis of apoptosis in naked mole-rat cells transfected with SV40 large T antigen (LT) or its mutant derivatives K1, which binds p53 family of proteins, and Δ434, which binds pRb family members. (A) Apoptosis in naked mole-rat skin fibroblasts (NMR SF) transfected with the plasmids encoding large T antigen constructs. Apoptosis was assayed on days 8 (black bars) and 14 (white bars) after transfection, using TUNEL. Day 14 is the time when cells start entering early contact inhibition. Striped bars correspond to cells grown in the presence of 5 μM apoptosis inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK for 14 days. (B) Same experiment as in (A) done with naked mole-rat lung fibroblasts (NMR LF). (C) Apoptosis in mouse skin fibroblasts (MSF) transfected with the plasmids encoding large T antigen constructs. Apoptosis was assayed on days 8 (black bars) and 14 (white bars) after transfection, using TUNEL. (D) Same experiment as in (C) with mouse lung fibroblasts (MLF). (E) Analysis of cell proliferation in naked mole-rat skin fibroblasts in the presence of 5 μM apoptosis inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK. Corresponding growth curves without Z-VAD-FMK are shown in Fig. 3A. Cells were transfected with the plasmids encoding large T antigen constructs and seeded on grided plates. Cell numbers were counted daily. The experiments were repeated at least three times and error bars show standard deviations. (F) Analysis of cell proliferation in naked mole-rat lung fibroblasts in the presence of ZVAD-FMK as described in (E). Corresponding growth curves without ZVAD-FMK are shown in Fig. 3B. All experiments were repeated three times, and error bars, standard deviations.