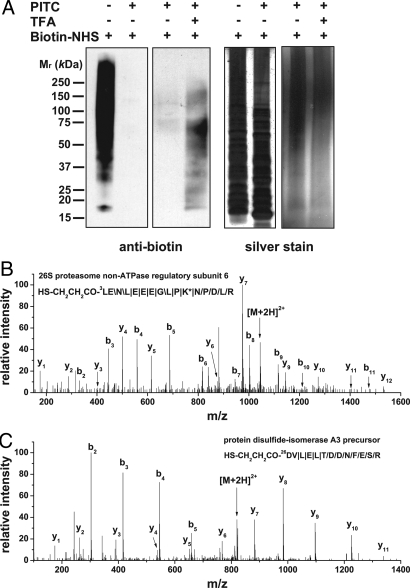
Fig. 4.
Identification of protein N-termini from a complex mixture using N-CLAP. (A) Evaluation of the completeness of PITC and TFA treatment on Jurkat T cell lysate. The amine content of a Jurkat T cell lysate is monitored by Western blotting with a biotin antibody at different stages in the N-CLAP protocol. Note that the exposure time for the right panel is much longer than for the left panel to detect the recovered signal after TFA treatment. Silver staining showed similar loading. (B and C) Representative MS/MS spectra of 2 N-CLAP peptides from Jurkat T cell lysate. The sequence map of the peptides, the N-terminal modification, the position of the first amino acid in the coding sequences, and the protein names are indicated in the spectra. PITC modification on lysine is indicated by an asterisk. In B, the N-CLAP peptide starts from the third amino acid from the coding sequence, which indicates that the initial methionine is removed from the nascent protein. However, in C the N-CLAP peptide starts from the 26th amino acid from the coding sequence, which indicates that the first 24 aa are removed in the nascent protein because the N-CLAP removes one additional N-terminal amino acid. The symbols \, /, and | represent b-ions, y-ions, and both b-ions and y-ions, respectively.