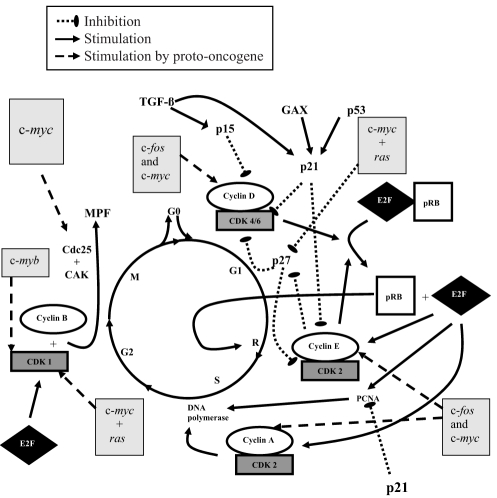
Figure 4).
Overview of the most important steps of cell cycle regulation. The key regulatory proteins are the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) proteins, which are activated at specific time points of the cell cycle. To be active, CDK needs association with cyclin to form a holoenzyme complex. Different cyclins are required at different steps of the cell cycle. CDK activity is also regulated by cell cycle inhibitory proteins called cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors (CKIs), which conteract CDK activity. Also shown are proto-oncogenes: c-fos, c-myb, c-myc and ras. Their gene products play a major role in the expression of specific regulatory proteins for the progression of the cell cycle. CAK CDK-activating kinase; GAX Growth arrest-specific homeobox; MPF Mitosis-promoting factor; PCNA Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; pRB Retinoblastoma gene product; TGF-β Transforming growth factor-beta