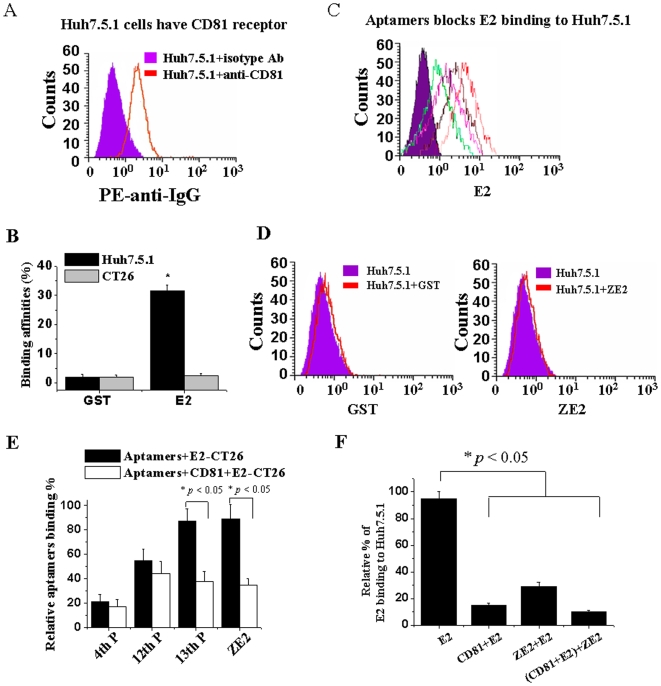
Figure 5. DNA aptamer ZE2 and viral receptor CD81 share similar binding sites on HCV E2.
(A) CD81 molecules are expressed on the cellular surface of hepatocytes Huh7.5.1; flow cytometric analysis with PE-labeled anti-CD81 antibody. PE-conjugated rat IgG1 was used as an isotype-matched control antibody (Ab). (B) HCV E2 had a much higher binding affinity for Huh7.5.1 than CT26 cells by flow cytometric analysis. E2-GST or GST proteins were preincubated with 1×106 Huh7.5.1 or CT26 cells, respectively. Anti-GST antibody and FITC-anti-IgG were added and analyzed by flow cytometric analysis. (C) Different pools of aptamers or single DNA aptamer ZE2 can block HCV E2 protein binding to Huh7.5.1 cells. (D) GST and ZE2 do not bind to huh7.5.1 cells by flow cytometric analysis. (E) CD81 competitively blocked FITC-aptamer binding to E2-CT26 cells by flow cytometric analysis. (F) Both ZE2 and CD81 competitively blocked E2 binding to Huh7.5.1 cells, as determined by flow cytometry with FITC-conjugated anti-E2 antibody. All data are mean±SEM from six separate experiments.