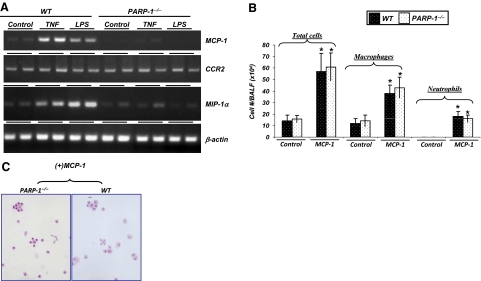
Figure 2.
Association between the effect of PARP-1 gene deletion on TNF- or LPS-induced inflammatory cell airway recruitment to effects on expression of MCP-1 and MIP-1α. (A) C57BL/6 WT or PARP-1−/− mice were subjected to a single intratracheal administration of LPS or TNF in 50 μl saline. Six hours after treatment, mice were killed, and whole lungs were collected and subjected to RNA extraction followed by cDNA generation. Prepared cDNA was subjected to RT-PCR for MCP-1, CCR2, MIP-1α, or β-actin. (B and C) C57BL/6 WT or PARP-1−/− mice (as in A) were subjected to a single intratracheal administration of MCP-1 (100 ng/mouse) in 50 μl saline or saline alone. Twenty-four hours after treatment, BALF were collected and centrifuged; cells were then differentially stained with H&E and visualized by light microscopy, followed by a count of total cells, neutrophils, and macrophages. Data are given as means ± sd of values obtained from at least four mice/group. *, Difference from untreated control mice, P < 0.01.