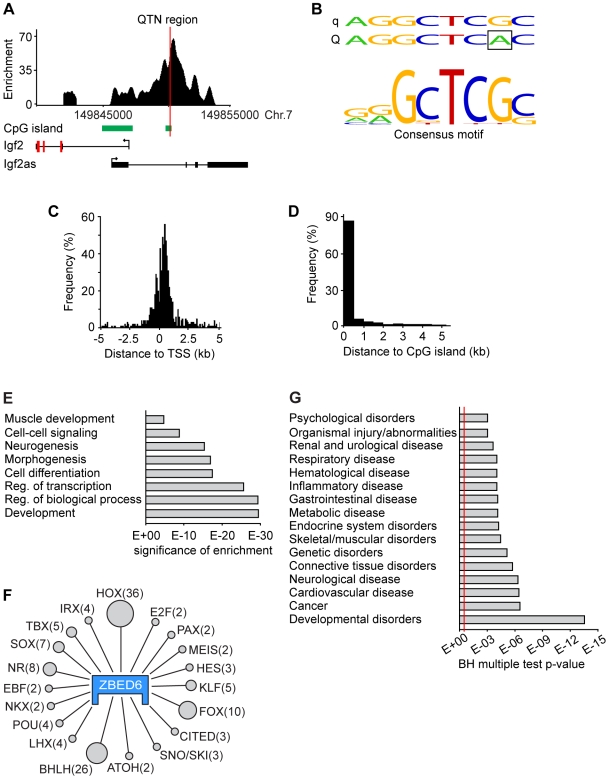
Figure 6. ChIP sequencing using mouse C2C12 cells.
(A) ChIP-sequencing peak around the quantitative trait nucleotide (QTN) position in an intron of Igf2. (B) ZBED6 binding motif in Igf2 and consensus ZBED6 motif based on peaks within 5 kb of transcription start sites (TSS) and with at least 25 overlapping fragments but excluding the binding site at Igf2. (C and D) ChIP-sequencing peaks are preferentially located in the near vicinity of (C) TSS and (D) CpG islands. (E) Gene Ontology categories highly enriched among the genes bound by ZBED6. Ontology terms are shown on the y axis; p-values for the significance of enrichment are on the x axis. (F) Overrepresented transcription factor families bound by ZBED6, including homeobox proteins (HOX), paired-like (PAX), HOX factors (MEIS), hairy and enhancer of split protein (HES), krueppel C2H2 zinc finger (KLF), Forkhead box (FOX), cbp/p300-interacting transactivator (CITED), SNO and SKI oncogenes (SNO/SKI), atonal homolog (ATOH), basic helix-loop-helix (BHLH), LIM homeobox (LHX), POU domain containing classes 3 and 4 (POU), NK transcription factor related (NKX), early B-cell factor (EBF), nuclear receptor (NR), SRY box (SOX), T-box (TBX), and Iroquois homeobox protein (IRX). The number of transcription factor genes associated with ZBED6 binding sites is indicated beside each family name. (G) Results of Ingenuity Pathways Analysis showing that putative downstream targets of ZBED6 are significantly associated with different diseases in humans. p-values for nonrandom association were calculated using the Fisher exact test, followed by a Benjamini-Hochberg correction for multiple testing. The red line indicates the 5% significance threshold.