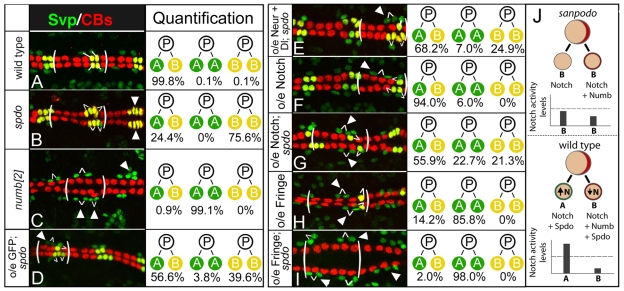
Fig. 8.
spdo facilitates Numb-mediated inhibition of Notch signaling during asymmetric divisions in the heart. (A) Wild-type pattern of sibling Svp-lacZ+ pericardial cells (green, ‘A’ cell) and cardioblasts (CBs; yellow, ‘B’ cell) in the stage 16 heart. In all panels one segment is bracketed, and white lines identify sibling relationships. (B) In spdo mutant embryos both Svp-lacZ+ daughter cells normally adopt the cardioblast or ‘B’ fate (yellow, arrowheads). (C) In numb mutant embryos both daughter cells adopt the pericardial or ‘A’ fate (green, arrowheads). (D,E) twist-GAL4-mediated expression of GFP (D), or Neuralized and Delta (E), in spdo mutant embryos causes both daughter cells to adopt the ‘A’ fate at low frequency (arrowhead), and increases the frequency of both daughter cells adopting alternate fates (‘A/B’). Note GFP overexpression has no effect on any other lineage tested (Fig. 3, see Tables S2 and S3 in the supplementary material). (F) Notch overexpression in wild type induces both daughter cells to adopt the ‘A’ fate at low frequency (arrowhead). (G) Notch overexpression in spdo mutant embryos increases the frequency at which both daughter cells adopt the ‘A’ fate (arrowheads). (H) Fringe overexpression in wild type directs both daughter cells to adopt the ‘A’ fate most of the time (arrowheads). (I) Fringe overexpression in spdo mutant embryos directs both daughter cells to adopt the ‘A’ fate (green, arrowheads) essentially all the time (arrowheads). Anterior, left. Quantification of sibling fates. n>800 sibling pairs assayed per genotype, except for numb (n=200). See also Table S3 in the supplementary material. (J) Model of spdo function during asymmetric divisions. Top, in spdo mutant embryos Notch signaling activity remains below the threshold level (dotted line) required to induce the ‘A’ fate, and both daughter cells adopt the ‘B’ fate. Bottom, in the absence of Numb, Spdo amplifies Notch signaling activity above the threshold required to induce the ‘A’ fate. In the presence of Numb, Spdo facilitates the ability of Numb to inhibit Notch signaling ‘B’ daughter cell, thereby reducing signaling activity below that observed in the absence of spdo.