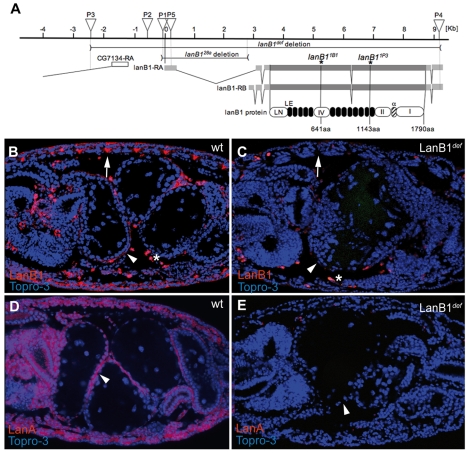
Fig. 1.
Molecular description of LanB1 mutant alleles and distribution of the LanB1 protein. (A) Schematic representation of the LanB1 genomic region. Both laminin β transcripts (LanB1-RA and LanB1-RB) with their coding and untranslated regions are represented in dark and light grey horizontal bars, respectively. The white box represents the 5′ UTR of the gene CG7134. The localisations of transposon insertions appear as inverted triangles [P1=P(EP)EP2178, P2=EP600, P3=P{XP}d04880, P4=PBac{RB}LanB1e02263, P5=l(2)k05404]. The horizontal lines correspond to the genomic region deleted in the LanB128a allele and the deficiency LanB1def. Asterisks indicate the positions of stop codons in the LanB11B1 and LanB11P3 alleles. Conserved domains are schematised as follows: white, from left to right, LanB1 N-terminal domain (LN), domain IV, domain II and domain I; black, 13 laminin-type EGF-like domains (LE); and stripped, the alpha domain. In all figures, embryos are oriented with anterior to the left. (B) In stage 16 wild-type embryos, LanB1 (red) is found in BMs surrounding most tissues (arrowhead) and at muscle attachment sites (arrow). (C) This expression is lost in maternal and zygotic homozygous LanB1def mutant embryos. (D) In wild-type embryos, LanA (red) is found at BMs. (E) This expression is not detected in LanB1def mutant embryos. In all figures, the nuclear marker TO-PRO 3 is in blue. wt, wild type.