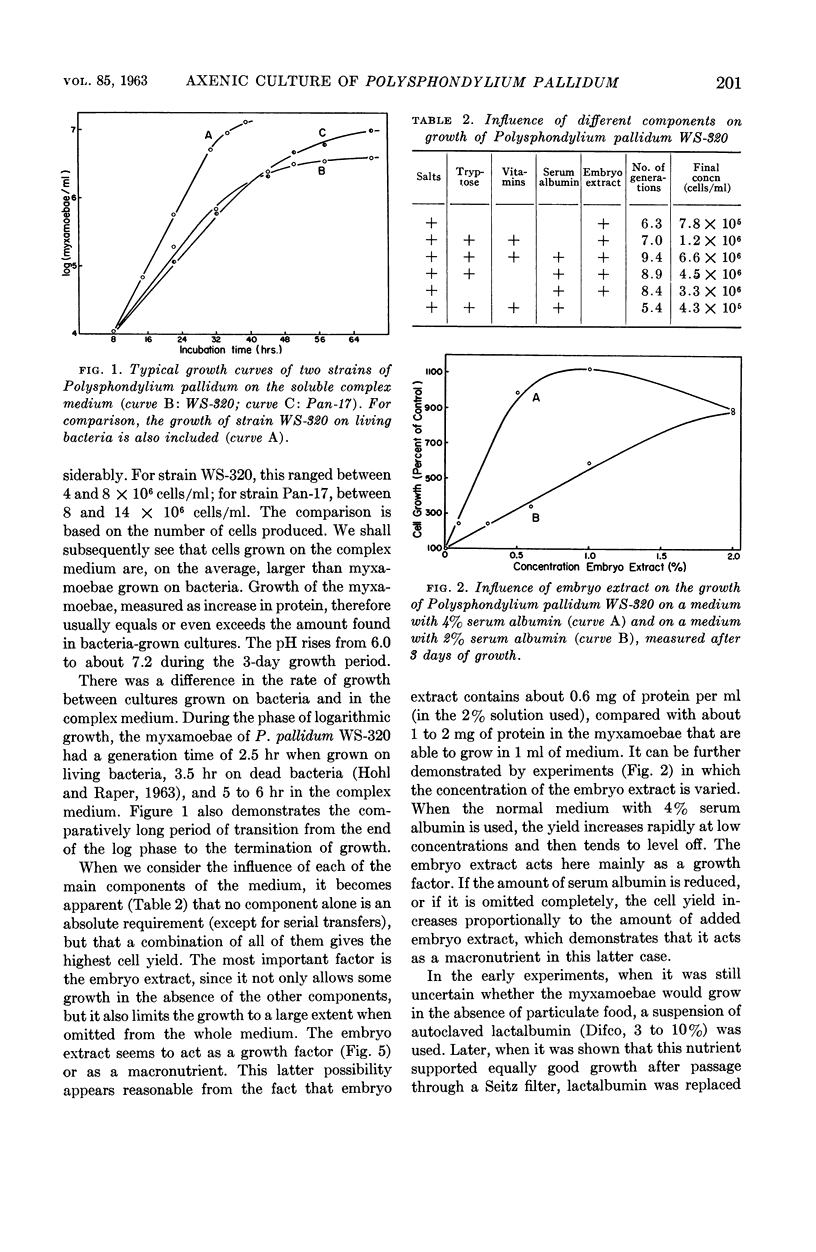
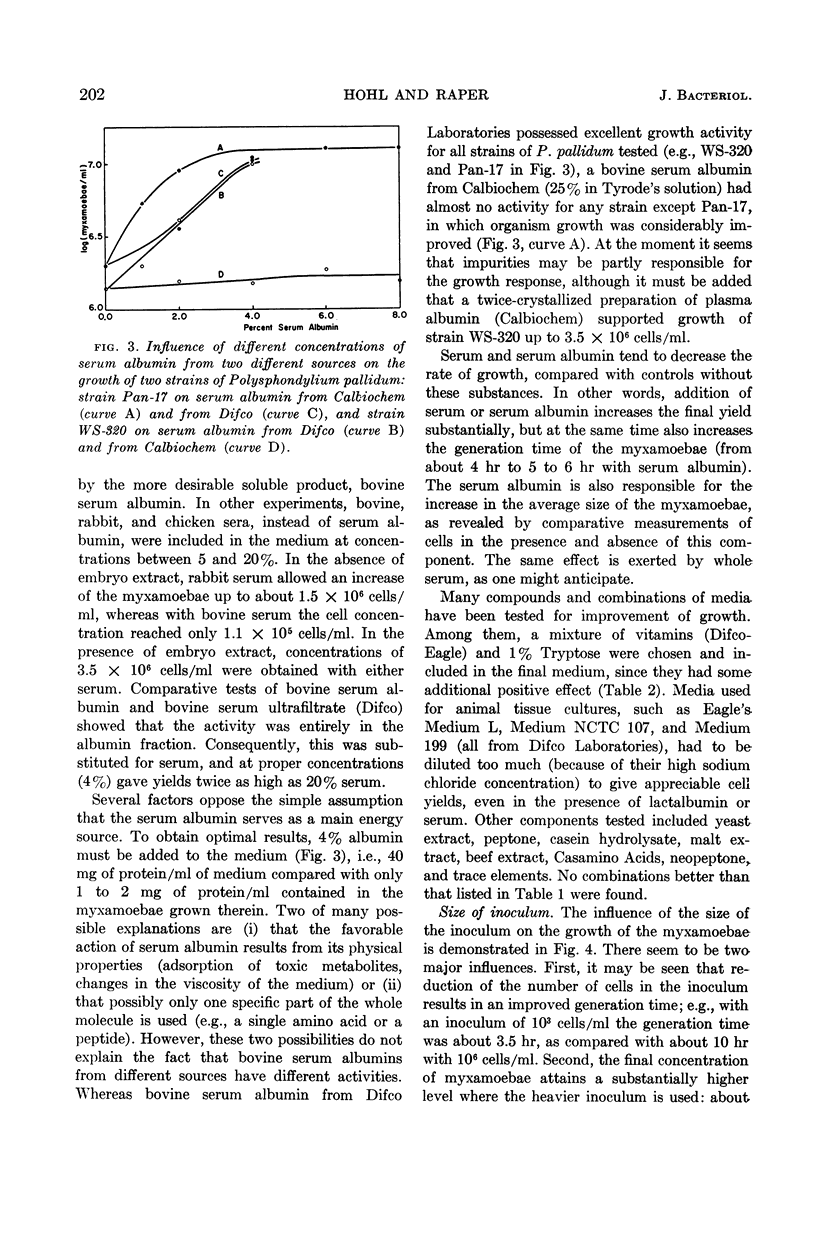
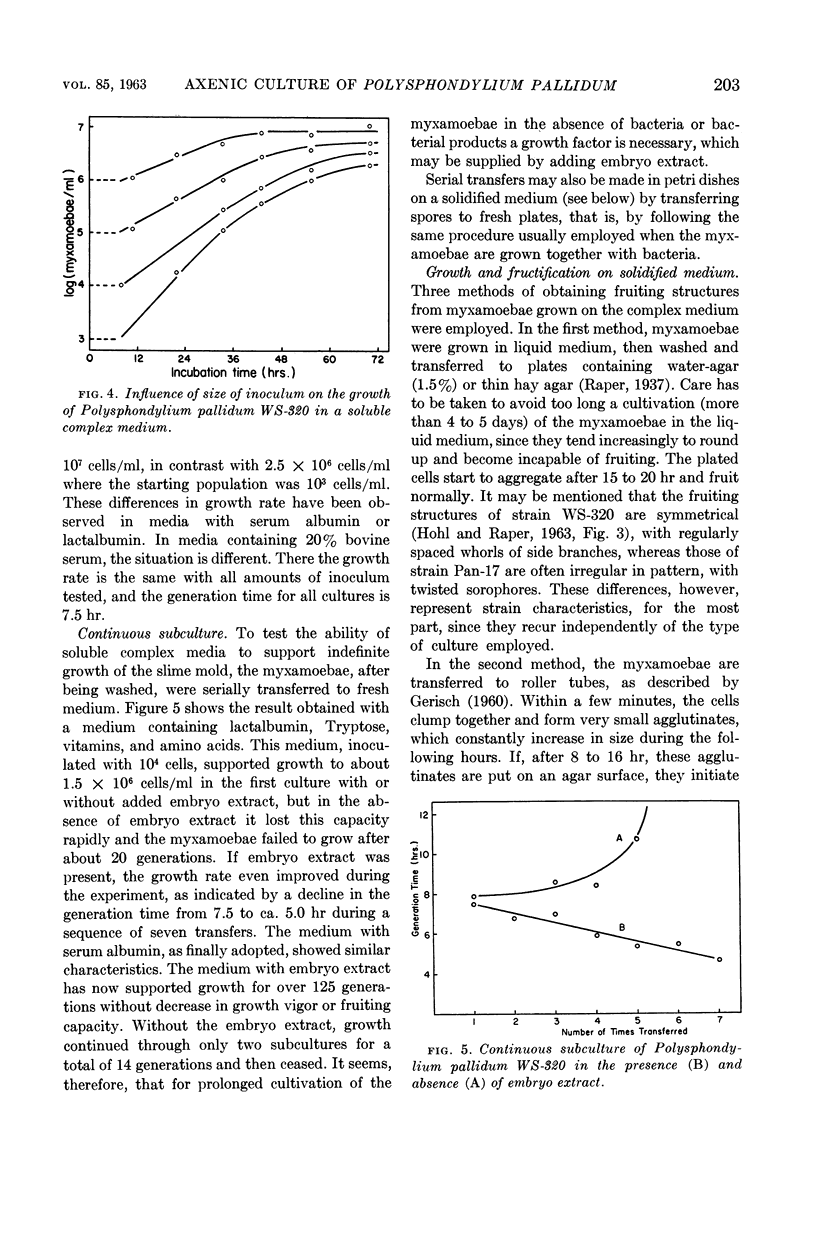
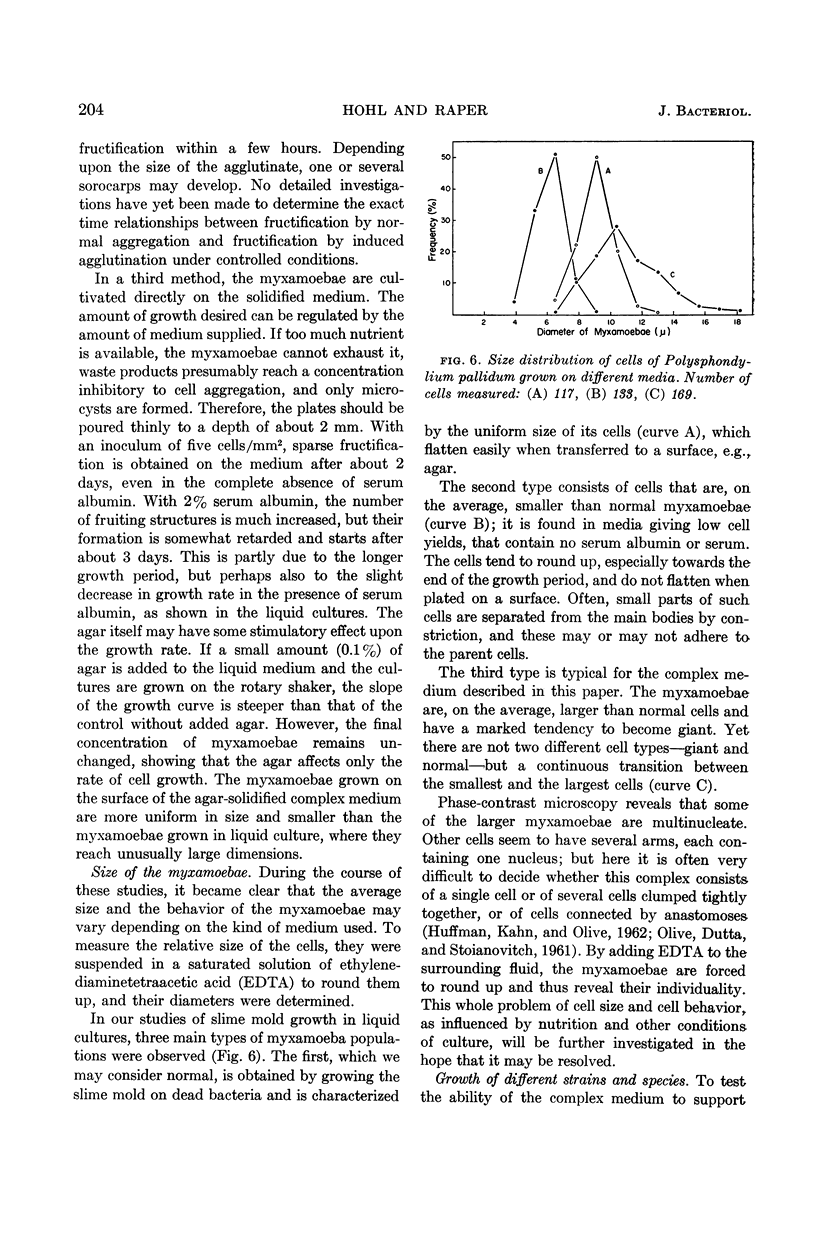
Abstract
Hohl, Hans-Rudolf (University of Wisconsin, Madison) and Kenneth B. Raper. Nutrition of cellular slime molds. II. Growth of Polysphondylium pallidum in axenic culture. J. Bacteriol. 85:199–206. 1963.—Several strains of Polysphondylium pallidum were grown on a liquid soluble medium in axenic culture. The medium contained embryo extract, serum albumin, Tryptose, dextrose, vitamins, and salts. The final cell yield was about 6–11 × 106 cells/ml, depending on the strain. The generation time was usually about 5 to 6 hr. The myxamoebae were grown for over 125 generations on this soluble complex medium without decrease in growth vigor or loss of their capacity to form normal fructifications when removed to an appropriate surface (e.g., agar). Thus the whole life cycle of this species was completed in the absence of any bacteria or bacterial products. Other species of the Dictyosteleaceae grew less well or failed to grow in the liquid medium described.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DANIEL J. W., KELLEY J., RUSCH H. P. Hematin--requiring plasmodial myxomycete. J Bacteriol. 1962 Nov;84:1104–1110. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.5.1104-1110.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Nutrition needs of mammalian cells in tissue culture. Science. 1955 Sep 16;122(3168):501–514. doi: 10.1126/science.122.3168.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOHL H. R., RAPER K. B. Nutrition of cellular slime molds. I. Growth on living and dead bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jan;85:191–198. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.1.191-198.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUFFMAN D. M., KAHN A. J., OLIVE L. S. Anastomosis and cell fusions in Dictyostelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jul 15;48:1160–1164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.7.1160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPER K. B. Isolation, cultivation, and conservation of simple slime molds. Q Rev Biol. 1951 Jun;26(2):169–190. doi: 10.1086/398077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUSSMAN M., BRADLEY S. G. A protein growth factor of bacterial origin required by the cellular slime molds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 Aug;51(2):428–435. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90498-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


