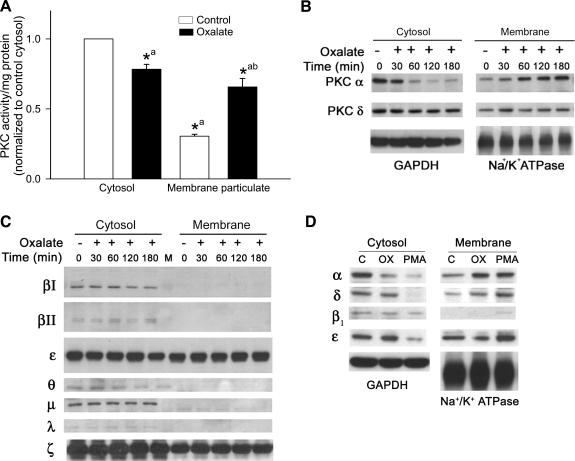
Fig. 2.
Effect of oxalate on PKC activity and PKC isoenzyme translocation in LLC-PK1 cells. A: LLC-PK1 cells were treated with or without 0.75 mM oxalate for 3 h, and PKC activity in the cytosol and membrane particulate fraction was determined. Data are normalized to cytosolic control, and values are expressed as means ± SE. Comparisons shown: a, significant compared with cytosolic control; b, significant compared with membrane control. *P < 0.05; n = 6. B: effect of oxalate on translocation of PKC-α and -δ. LLC-PK1 cells were treated with oxalate for different time periods. Lysates of cytosolic and membrane fractions were analyzed for PKC-α and -δ expression by Western blotting. A typical Western blot from 1 of 4 experiments is shown. GAPDH was used as a cytosolic loading control and Na+-K+-ATPase as a membrane loading control. C: effect of oxalate on translocation of endogenous conventional PKCs, novel PKCs, and atypical PKCs. LLC-PK1 cells were treated with oxalate for different time periods. Lysates of cytosolic and membrane fractions were analyzed for PKC isoenzyme expression by Western blotting. A typical blot from 1 of 4 experiments is shown. D: effect of PMA or oxalate on PKC isoenzyme translocation from cytosol to membrane fraction. LLC-PK1 cells were treated with PMA (1 μM) or oxalate (0.75 mM) for 3 h. Lysates of cytosolic and membrane fractions were analyzed for PKC isoenzyme expression by Western blotting. GAPDH was used as a cytosolic loading control and Na+-K+-ATPase as a membrane loading control. A typical blot from 1 of 4 experiments is shown.