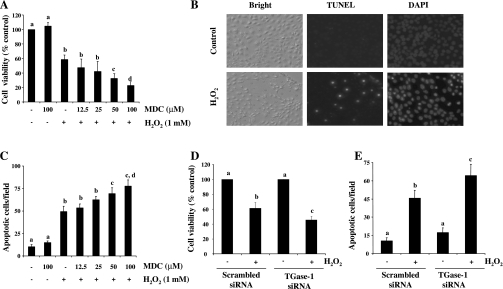
Fig. 1.
Effect of transglutaminase-1 (TGase-1) inhibition on H2O2-induced apoptosis in RPTC. Renal proximal tubular cells (RPTC) cells were treated with monodansylcadervine (MDC; 12.5–100 μM) for 1 h and then exposed to 1 mM of H2O2 for 4 h. Cell viability was assessed by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay (A). DAPI and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP-mediated nick-end labeling technology (TUNEL) staining was performed and photographed (B). Cells stained with DAPI and apoptotic cells were counted from 4 different fields in each sample (×200; C). RPTC were transfected with scrambled small interference (si)RNA or TGase-1-specific small interference (si)RNA. At 12 h after transfection, cells were starved for an additional 24 h and then treated with 1 mM H2O2 for 4 h. Cell viability and apoptosis were assessed by MTT assay (D) and DAPI staining (E), respectively. Values are means ± SD of 3 independent experiments conducted in triplicates and expressed as the percentage of control (A and D) or total apoptotic cells per field (C and E). Bars with different letters are significantly different from one another (P < 0.05).