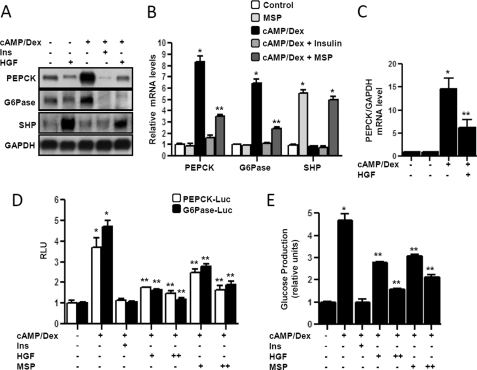
FIGURE 1.
Inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis by HGF and MSP in primary hepatocytes. A–C, primary rat hepatocytes (A and B) and primary human hepatocytes (C) were pretreated with HGF (50 ng/ml, A and C), insulin (10 nm, 1 h), and MSP (100 ng/ml, B) for 3 h followed by treatment with cAMP (500 μm) and Dex (100 nm) treatment for 3 h in the continuous presence or absence of HGF and MSP. Total RNA was isolated for Northern hybridization (A) and qPCR analysis (B and C). Data represent means ± S.D. of three individual experiments. *, p < 0.001 and **, p < 0.05 compared with untreated control and cAMP/Dex treated cells, respectively. D, AML12 cells were transfected with pepck and Glc-6-Pase-Luc (200 ng) for 24 h followed by treatment with cAMP (500 μm) and Dex (100 nm) treatment for 3 h in the continuous presence or absence of HGF (50 and 100 ng/ml), MSP (100 and 200 ng/ml), or insulin as mentioned previously. Experiments were done in triplicate, and data are expressed in RLU and as the fold activation relative to the control. Data represent mean ± S.D. of three individual experiments. *, p < 0.05 and **, p < 0.001 compared with untreated control and cAMP/Dex-treated cells, respectively. E, measurement of glucose production. Experiments were performed as described in A and B, using glucose-free media supplemented with gluconeogenic substrate sodium lactate (20 mm) and sodium pyruvate (1 mm). Data represent mean ± S.D. of four individual experiments. *, p < 0.001 and **, p < 0.001 compared with untreated control and cAMP/Dex treated cells, respectively. G6Pase, Glc-6-Pase; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.