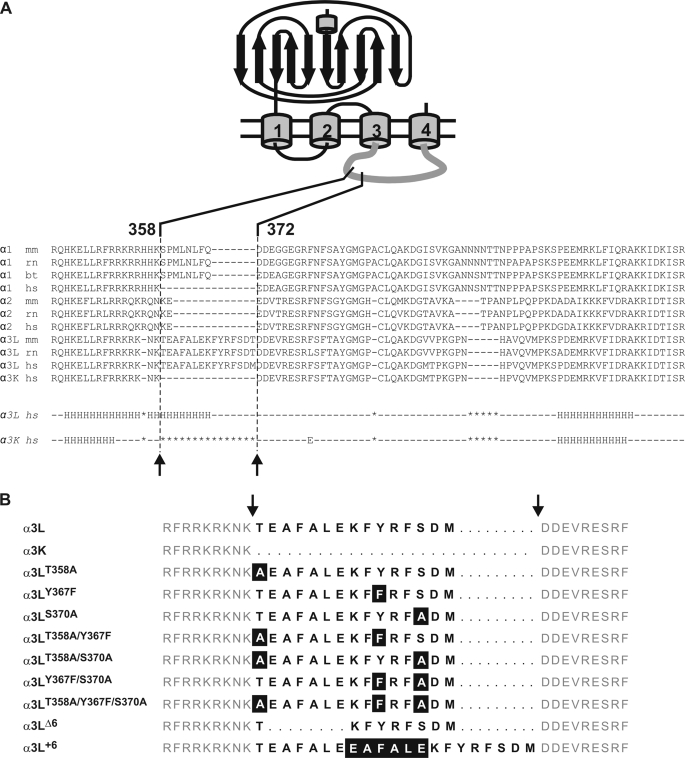
FIGURE 1.
GlyR α subunit sequences and constructs. A, alignment of various receptors in the TM3–4 loop region. The alternatively spliced region is indicated. Note the large sequence divergence in the region of the insert. Lower panel, Jpred (34) secondary structure predictions for α3L (middle row) and α3K (bottom row). Use of several other prediction routines from the EXPASY server gave similar results. The α-helical content of α3L according to the prediction is ∼38% (35 of 92 residues), in good agreement with secondary structure analysis by CD spectroscopy. B, glycine receptor a3 variants used in the study; the one-letter codes for amino acids are used. The alternatively spliced 15-residue segment (positions 358–372) is indicated by bold letters, and flanking sequences are shown in gray. Deleted residues within the spliced segment are shown as bold dashes, and flanking sequences are aligned on either side of the insert. Mutated residues are highlighted.