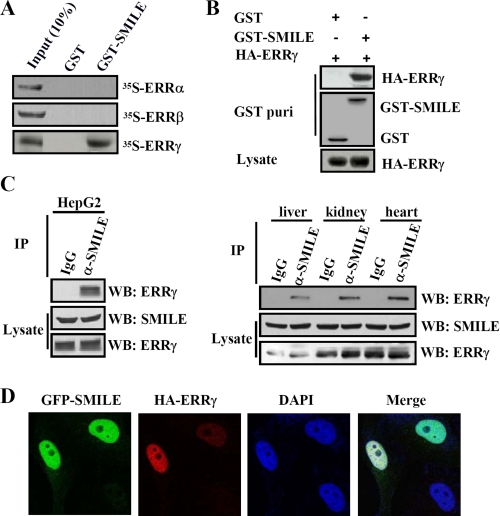
FIGURE 1.
Interaction and colocalization of SMILE with ERRγ. A, in vitro GST pulldown assays. 35S-Radiolabeled ERRα, ERRβ, or ERRγ proteins were incubated with GST or GST-SMILE fusion proteins. The input lane represents 10% of the total volume of in vitro-translated proteins used for binding assay. Protein interactions were detected via autoradiography. B, in vivo interaction between exogenous ERRγ and SMILE. HepG2 cells were cotransfected with pSG5-HA-ERRγ and pEBG-SMILE (GST-SMILE) or pEBG alone (GST). Protein interactions were examined via in vivo GST pulldown. The top and middle panels (GST puri) show GST beads-precipitated HA-ERRγ and GST fusion proteins, respectively. The bottom panel shows the protein expression levels of HA-ERRγ in cell lysates. C, in vivo interaction of endogenous ERRγ and SMILE. Coimmunoprecipitation assays were performed using cell extract from HepG2 cells, mouse liver, kidney, and heart tissues with anti-SMILE antibody. Endogenous SMILE was immunoprecipitated (IP) with ERRγ (upper panels). The proteins in the cell lysates (middle and lower panels) were analyzed with Western blot (WB) analysis using indicated antibodies. D, colocalizations of SMILE with ERRγ. HeLa cells were transfected with 0.1 μg of expression vectors encoding GFP-SMILE and HA-ERRγ. HA fusion proteins were detected with dye Alexa 594-conjugated anti-HA monoclonal antibody. The cell images were captured under ×400 magnifications. The data shown are representative of at least three independent experiments. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.