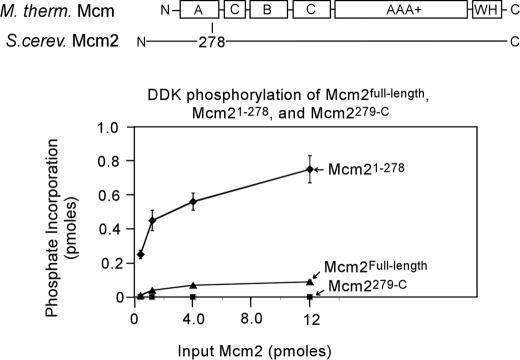
FIGURE 3.
DDK phosphorylates the N-terminal region of Mcm2. A structure-based sequence alignment with Sulfolobus solfataricus Mcm was used to divide Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mcm2 into two segments, an N-terminal fragment encompassing the nonconserved N-terminal region and most of domain A (Mcm2-(1–278)) and a C-terminal fragment encompassing the rest of the protein (Mcm2-(279-C)). S. cerevisiae Mcm2Full-length, Mcm2-(1–278), or Mcm2-(279-C) was incubated with 50 ng of DDK and [γ-32P]ATP in a volume of 10 μl for 30 min at 30 °C, and the reactions were then analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by phosphorimaging. The results were quantified, and the fraction of phosphate incorporation is plotted as a function of input in picomoles.