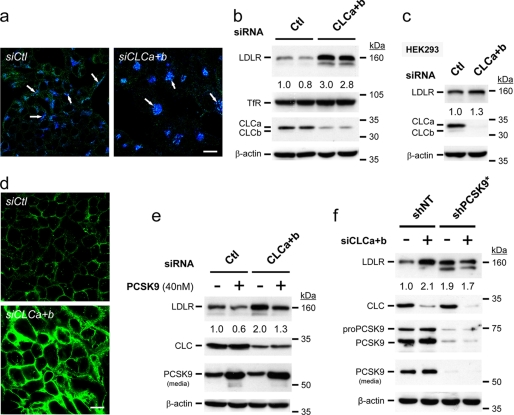
FIGURE 5.
KD of CLCs increases endogenous LDLR levels only in PCSK9-expressing cells. HepG2 or HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with either a nonsilencing siRNA (siCtl) or with siRNAs against both CLC a and b isoforms (siCLCa+b). a, immunocytochemistry analyses confirmed that KDCLCs (green) results in the clustering of the cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor, characteristic of disruption of the intracellular Golgi-lysosomal pathway (blue; see arrows). b and c, at 72 h after transfection, HepG2 and HEK293 cells were analyzed by Western blotting. d, immunocytochemistry under nonpermeabilizing conditions of cell surface LDLR (green) upon KDCLCs (siCLCa+b) compared with nonsilencing siRNA transfected cells (siCtl) is shown. e, at 48 h after transfection, addition of 40 nm exogenous PCSK9 enhances the degradation of LDLR irrespective of KDCLCs. (f) Effect of KDCLCs on LDLR protein levels in HepG2 cells with (shNT) or without (shPCSK9*) endogenous PCSK9 is shown. The 160 kDa band representing mature LDLR was quantified and normalized with those of actin. These data are representative of 3–6 independent experiments. Scale bars, 20 μm.