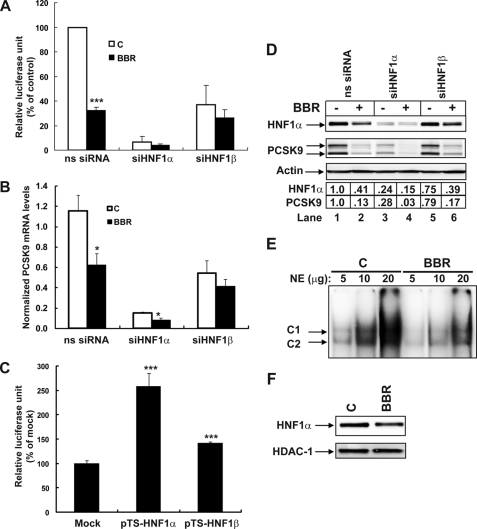
FIGURE 6.
Effects of siHNF1α and siHNF1β knockdown on PCSK9 transcription and protein expression in HepG2 cells untreated and treated with BBR. A, analysis of PCSK9 promoter activity in CL26 cells transfected with targeted siRNA or control nonspecific siRNA. Cells were treated with BBR at a concentration of 40 μm or its vehicle (0.1% DMSO) as control for 24 h prior to cell lysis. Data represent the means ± S.D. derived from four separate transfection experiments. B, real-time reverse transcription-PCR analysis of PCSK9 mRNA levels in HepG2 cells after siRNA transfection of 2 days followed by BBR treatment of 24 h. Data represent the means ± S.E. derived from three separate transfection experiments. C, D4 was cotransfected with either pTS-HNF1a, pTS-HNF1b, or with a mock vector along with pRL-SV40 in a DNA ratio of 2:1:0.2 into HepG2 cells. Dual luciferase activities were measured. The normalized luciferase activity in D4-transfected cells with the mock vector is expressed as 100%, and luciferase activities in cells transfected with other expression vectors are plotted relative to that value. D, Western blot analysis of HNF1α, PCSK9, and β-actin in total cell lysates of siRNA-transfected HepG2 cells without and with BBR treatment. The HNF1α and PCSK9 bands were quantified using an imaging program of Kodak Image Station 4000R. Values were normalized to β-actin and were graphed relative to untreated cells without siRNA transfection. E, indicated amounts of nuclear extracts prepared from untreated or BBR-treated cells were incubated with the 32P-labeled PCSK9-HNF1 probe and analyzed by EMSA. F, HepG2 cells were treated with BBR (40 μm) or its vehicle 0.1% DMSO as control for 24 h. Nuclear extracts were isolated. 50 μg of nuclear proteins from each sample was analyzed by Western blotting with HNF1α antibody, followed by blotting the membrane with anti-HDAC1 as a loading control. The data shown in C–F are representative of 2–3 separate experiments with similar results.