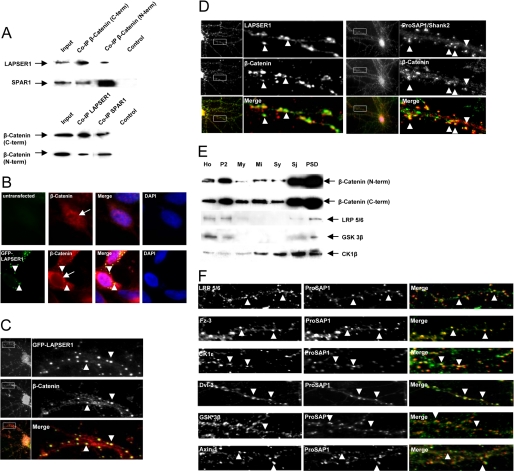
FIGURE 3.
LAPSER1 is part of a postsynaptic complex that contains β-catenin and other important Wnt pathway molecules. A, coimmunoprecipitation experiments with rat brain homogenate revealed that β-catenin interacts with LAPSER1 in brain. Two commercially available antibodies directed against the C- and N-terminal part of β-catenin were used for precipitation, and LAPSER1 could be detected in the precipitate. Moreover, SPAR1 was also found within the precipitate. Vice versa, experiments showed that after the precipitation with LAPSER1- or SPAR1 antibodies, β-catenin can be detected in the precipitate. B and C, overexpression of GFP-LAPSER1 in COS-7 cells or hippocampal neurons led to a recruitment of endogenous β-catenin (also shown in an untransfected COS-7 cell) into the GFP-LAPSER1 clusters in the cell cytoplasm and at postsynaptic sites (arrowheads). In contrast to untransfected cells, the overexpression of LAPSER1 led to the complete nuclear elimination of endogenous β-catenin that seemed now to be concentrated perinuclear (arrows). D, the endogenous complex of LAPSER1 and β-catenin could be seen at postsynaptic sites in cultured hippocampal neurons (21 days) after double-immunostaining (arrowheads). The mainly postsynaptic localization of β-catenin is verified with the postsynaptic marker ProSAP1/Shank2. E and F, the Wnt pathway members β-catenin, LRP5/6, GSK-3β, and CK1ϵ were highly enriched toward the PSD fraction of rat brain homogenate. Moreover, these proteins as well as the Wnt pathway components Fz-3 (frizzled receptor 3) and Dvl-3 (dishevelled 3) could be detected in hippocampal cells concentrated as dot-like structures that overlay with the labeling of the postsynaptic marker protein ProSAP1/Shank2 indicating the postsynaptic localization of the molecules (arrowheads).