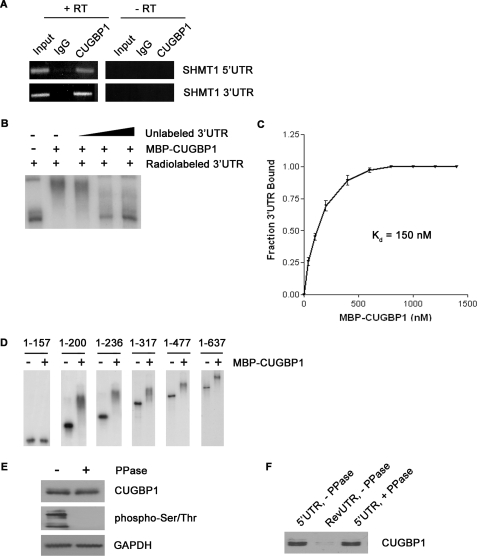
FIGURE 3.
The interaction of CUGBP1 with the SHMT1 UTRs. A, RNA was immunoprecipitated from UV-treated MCF-7 whole cell extract using an antibody against IgG (control for nonspecific binding) or CUGBP1. The RNA in lanes 1–3 (+RT) was reverse-transcribed into cDNA and then analyzed by PCR using primers specific to either the SHMT1 5′-UTR or the SHMT1 3′-UTR. The RNA in lanes 4–6 (−RT) did not undergo the reverse transcription step. Rather, they were analyzed directly by PCR to control for DNA contamination in the immunoprecipitates. Lanes 1 and 4 (Input) represent 1% of the RNA used in the immunoprecipitation. B, electrophoretic mobility shift assays were carried out in the presence of excess yeast tRNA to eliminate nonspecific binding of the probe, radiolabeled SHMT1 3′-UTR, and recombinant MBP-CUGBP1. A 10×, 50×, and 100× molar excess of unlabeled SHMT1 3′-UTR was also added in lanes 3, 4, and 5, respectively, to determine binding specificity. C, electrophoretic mobility shift assays were carried out using radiolabeled SHMT1 3′-UTR and increasing concentrations of MBP-CUGBP1. The fraction of the 3′-UTR bound by the recombinant protein was quantified using ChemiImager 4400 from Alpha Innotech Corp. The dissociation constant (Kd) was determined using GraphPad Prism. D, electrophoretic mobility shift assays were carried out using radiolabeled SHMT1 3′-UTR truncation mutants in the absence and presence of MBP-CUGBP1. The nucleotides of the 3′-UTR that comprise the truncation mutant are listed above each gel. The nucleotide at the 5′-end of the 3′-UTR is labeled 1. The nucleotide at the 3′-end of the 3′-UTR is labeled 637. E, MCF-7 whole cell extract was either not treated or treated with λ-phosphatase (PPase) and analyzed by Western blot using antibodies against CUGBP1 and phosphorylated serine and threonine residues. GAPDH served as a control for equal protein loading. F, the extracts from E were applied to RNA affinity columns to which either the SHMT1 5′-UTR or the RevUTR had been attached. Proteins that bound to the UTRs were eluted and analyzed by Western blotting using an antibody against CUGBP1.