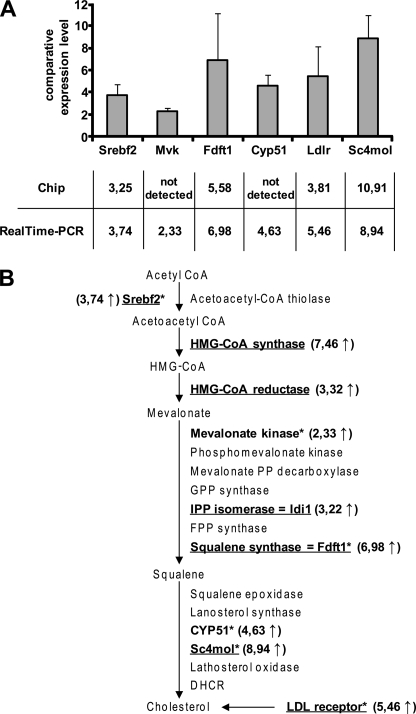
FIGURE 1.
22L prion infection of N2a cells induces increased transcription of genes regulated by Srebp2. Differential gene expression of genes involved in cholesterol synthesis is shown. A, up-regulation of Srebf2 (sterol regulatory element-binding factor 2), Mvk (mevalonate kinase), Fdft1 (farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyltransferase 1), Cyp51 (cytochrome P450, family 51), Ldlr (low density lipoprotein receptor), and Sc4mol (C4-sterol methyl oxidase) was determined by real time PCR in the 22L-infected clone 5 (passage 18) compared with mock-infected clone 5 (passage 18). All results were normalized to the RPII (RNA polymerase 2) expression levels. For triplicate experiments, the standard deviation is shown for each gene. The y axis denotes the comparative gene expression levels. B, overview of important genes in the cholesterol pathway activated by Srbp2 (17). Genes in boldface were found up-regulated in prion-infected N2a cells compared with mock-infected N2a cells either in the chip experiment (underlined) or as detected by real time PCR (marked with asterisks). Srebp2 is the limiting transcription factor of cholesterol synthesis. HMG-CoA, hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA; FPP, farnesyl diphosphate; IPP, isopentenyl diphosphate; GPP, geranyl diphosphate; DHCR, 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase.