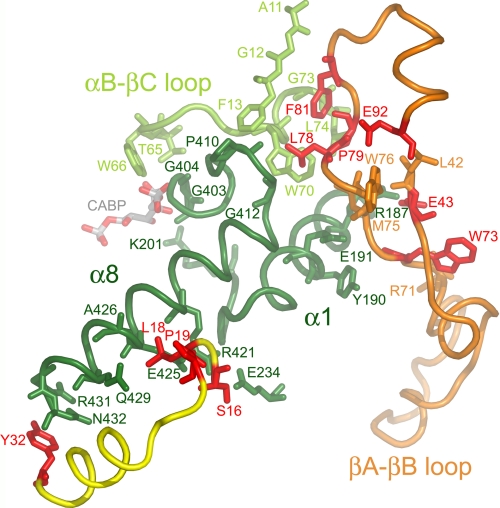
FIGURE 5.
Conserved small subunit residues (red) in the x-ray crystal structure of Chlamydomonas Rubisco (Protein Data Bank code 1GK8) (23). Looking down from the top of the Rubisco holoenzyme, the large subunit α/β-barrel is viewed from the side. Conserved small subunit residues from one small subunit (yellow ribbon) cluster near the carboxyl-terminal bottom (Tyr-32) and middle (Ser-16, Leu-18, and Pro-19) of large subunit α-helix 8 (dark green residues 413–432). Conserved small subunit residues Glu-43, Trp-73, Leu-78, Pro-79, Phe-81, and Glu-92 from a second small subunit (orange ribbon) cluster near the amino-terminal top of large subunit α-helix 8 or its preceding loop (dark green residues 403–412). Small subunit residues Glu-43 and Trp-73 are also in contact with α-helix 1 (dark green residues 182–194 and residues 195–201 following). Small subunit residues Leu-78, Pro-79, and Phe-81 are in contact with part of the loop between α-helix B and β-strand C from a neighboring large subunit (light-green residues 65–74). Large subunit active site residues Thr-65, Trp-66, Lys-201, Gly-403, and Gly-404 are in contact with the CABP transition state analog. A summary of contacts between the conserved small subunit residues and large subunit residues is provided in supplemental Table S1.