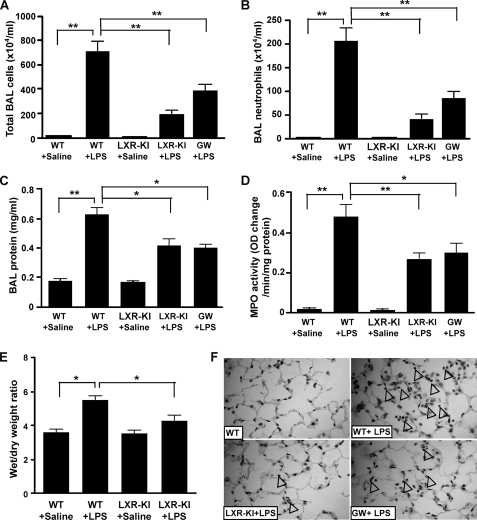
FIGURE 4.
Activation of LXR conferred resistance to LPS-induced lung injury. WT and LXR-KI mice received intranasal instillation of saline or LPS. The fifth group of WT mice was treated with GW3965 (GW, 20 mg/kg, daily, intraperitoneally) for 7 days before being treated with LPS. Twenty-four hours after LPS instillation, the mice were sacrificed, and the lungs were lavaged to collect the BAL fluids. A, the total BAL cell numbers were counted using a hemocytometer. B, polymorphonuclear neutrophils were stained with Wright solution, and their cell numbers were counted. C, the protein concentrations of the cell-free BAL supernatants were measured. D, lung homogenates were measured for the MPO activity. E, the wet to dry weight ratio of the lung tissues. F, hematoxylin and eosin staining of lung sections derived from mice treated with saline or LPS. Arrowheads indicate neutrophil infiltration (n = 6 for each group). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01, comparisons are labeled.