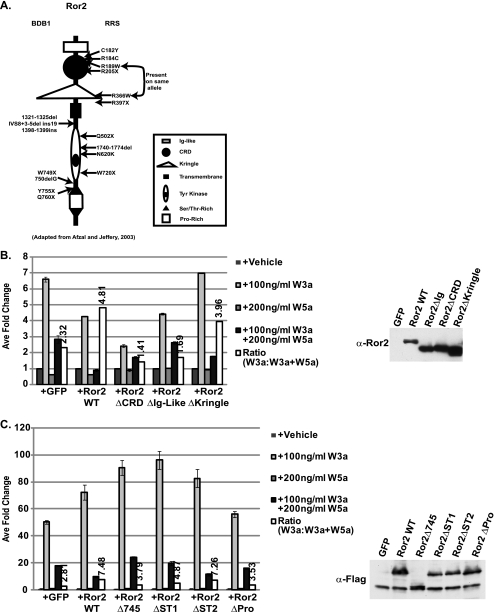
FIGURE 1.
Deletion of mRor2 extracellular and intracellular domains results in decreased Wnt5a-mediated inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. A, diagram of the major domains of the mRor2 receptor. B, extracellular domain deletion mutants of mRor2 (ΔCRD and ΔIg-like) show reduced ability to enhance Wnt5a-mediated inhibition. ∼40 h post-transfection with STF reporter and Ror2 variants, HEK293 cells were treated with vehicle, Wnt3a protein alone, Wnt5a protein alone, or Wnt3a protein plus Wnt5a protein for an additional 20 h. Following reporter assay, cell lysates were examined for receptor expression via Western blot analysis with α-Ror2 antibody. GFP, green fluorescent protein; WT, wild type. C, intracellular domain deletion mutants of mRor2 show reduced ability to enhance Wnt5a-mediated inhibition. Cells were transfected with Ror2 deletion variants described and treated as indicated above. Following reporter assay, cell lysates were examined for receptor expression via Western blot with α-FLAG antibody.