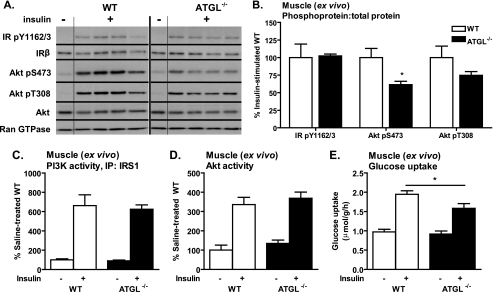
FIGURE 7.
Skeletal muscle insulin signaling and glucose transport ex vivo. A–D, for analysis of insulin signaling in skeletal muscle ex vivo, soleus muscles were dissected from 6- to 10-week-old female mice following a 6-h fast and incubated in the presence or absence of 33 nm insulin. A and B, insulin-stimulated site-specific phosphorylation of the IR, IRS1, and Akt as assessed by immunoblotting analysis (n = 3–5 per group). For quantification, phosphoproteins were normalized to total proteins. Ran GTPase served as loading control. C, IRS1-associated PI3K activity; and D, Akt activity (n = 3–9 per group). E, for analysis of glucose uptake into skeletal muscle ex vivo, soleus muscles were dissected from 9- to 13-week-old female mice following a 6-h fast (n = 9–11 per group) and assayed for uptake of 2-[3H]deoxyglucose in presence or absence of 33 nm insulin. Similar results were observed for EDL. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E. *, p < 0.05 for effect of genotype as determined by unpaired two-tailed Student's t test (B) or one-way ANOVA (C–E).