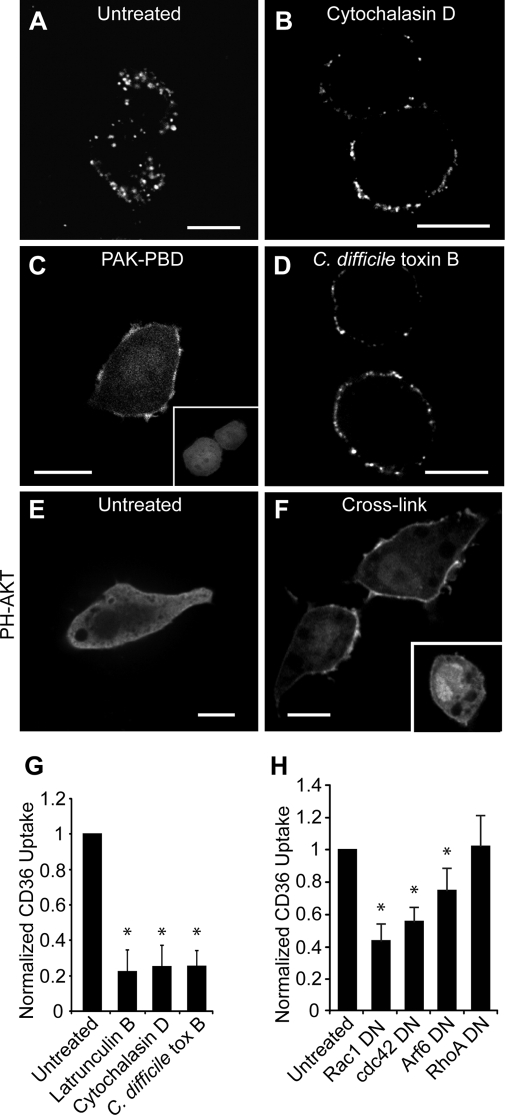
FIGURE 3.
Actin inhibitors block internalization of CD36. RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated as follows: no treatment (A), cytochalasin D (B), or C. difficile toxin B (D). CD36 receptors were then cross-linked, and cells were warmed, fixed, and imaged. Acid wash was omitted to preserve surface labeling. C, Rac1 activation was demonstrated by recruitment of PAK1-PBD-YFP to the membrane. RAW 264.7 cells transfected with PAK-PBD-YFP were imaged following CD36 receptor cross-linking with (C) or without (C, inset) anti-CD36 antibodies. E and F, cross-linking activates PI3K. RAW 264.7 cells transiently expressing PH-AKT-GFP were treated without (E) or with (F) CD36 cross-linking antibody and warming. F, inset, cross-linking was done in the presence of LY294002. To quantify CD36 internalization (G), the same assay was performed with the addition of two acid washes. Cells were warmed to 37 °C, and internalized CD36 was imaged live on a spinning disc microscope. H, to demonstrate dependence of CD36 internalization on Rho or Arf family small GTPases, RAW 264.7 cells were transfected with dominant negative (DN) DNA constructs of Rac1, Cdc42 Arf6 or RhoA, and internalized CD36 receptors were quantified as above. Scale bars, 10 μm. *, p < 0.05 compared with untreated control.