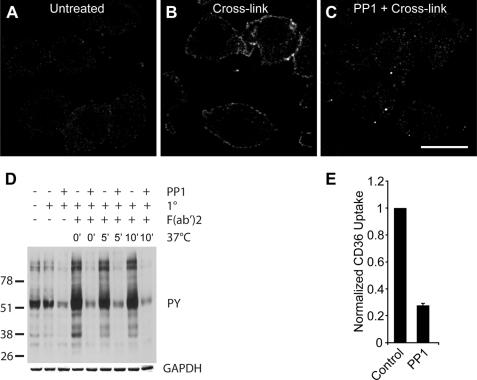
FIGURE 5.
Cross-linking of CD36 receptors causes tyrosine phosphorylation. A–C, RAW 264.7 cells untreated (A), cross-linked with anti-CD36 (B), or cross-linked after pretreatment with the Src family tyrosine kinase inhibitor PP1 (C) were fixed and stained for phosphotyrosine. Scale bar, 10 μm. D, immunoblot of tyrosine phosphorylation subsequent to CD36 cross-linking and internalization. RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated without or with PP1 followed by cross-linking of CD36 with primary IgA antibody in the cold, secondary F(ab′)2 antibody and warming for 0 min, 5 min, or 10 min. Immunoblot was probed for phosphotyrosine (4G10), stripped, and reprobed for GAPDH. E, dependence of CD36 internalization on tyrosine phosphorylation. RAW cells were pretreated without (control) or with PP1 prior to cross-linking of CD36 receptors and warming in the presence of PP1. Cells were acid-washed twice before fixation and imaging on a spinning disc confocal microscope. Data are normalized to the control.