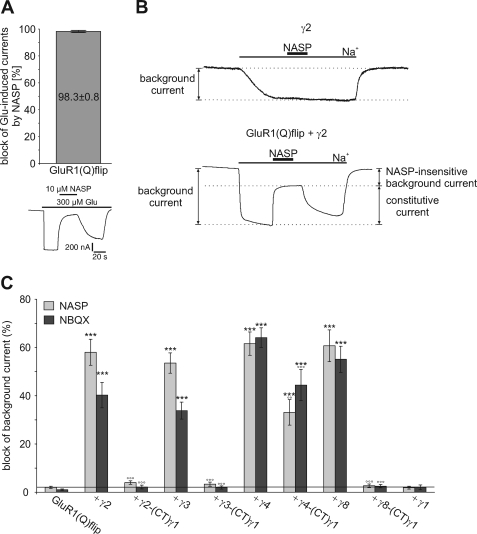
FIGURE 7.
Influence of wild-type and chimeric TARPs carrying the C-terminal domain of γ1 on constitutive channel openings of GluR1(Q)flip. A, mean block of glutamate-induced responses by 10 μm NASP of GluR1(Q)flip (n = 7). Data are shown as means (±S.E.). Additionally, a representative block of glutamate-induced responses by 10 μm NASP of GluR1(Q)flip is presented. The duration of agonist and NASP application is indicated by horizontal black bars. B, typical holding current trace of γ2 alone and GluR1(Q)flip coexpressed with γ2 in sodium-free Ringer's solution. Application of sodium-containing Ringer's solution triggered an inward current that could be partially blocked by NASP (10 μm, duration of application noted by black bar), thus indicating the fraction of constitutively open GluR1(Q)flip channels. C, mean block of background currents by NASP (gray columns) and NBQX (black columns), each at 10 μm, of GluR1(Q)flip alone and coexpressed with wild-type TARPs and TARP/γ1 C-terminal chimeras. The horizontal line marks the level of NASP block of GluR1(Q)flip alone. Data are shown as mean (±S.E.) of 10–14 oocytes (***, p < 0.005, significantly different from GluR1(Q)flip alone; °°, p < 0.01 and °°°, p < 0.005, significantly different compared with wild-type TARPs; Student's t-test).