FIGURE 3.
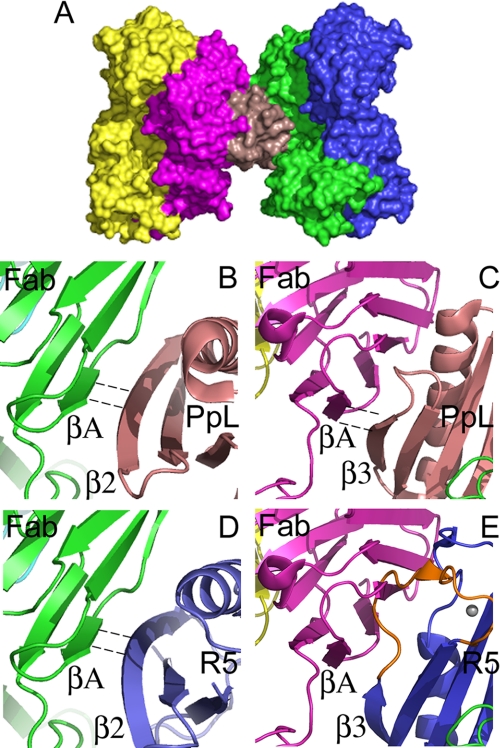
Modeling the interaction of the B1 domain of the Mub-R5 repeat with an IgG Fab domain. A, a molecular surface representation of the 1:2 ternary complex formed by a Protein L domain (PpL) with two human antibody Fab fragments (light red, PpL; green and magenta, Fab VL domains; and blue and yellow, Fab VH domains). Atomic coordinates were taken from PDB entry 1HEZ. B and C, close-up views of the molecular interfaces formed by the PpL domain in the 1:2 complex. The two interfaces have antiparallel (B) and parallel (C) hydrogen-bonding arrangements involving the β2 and β3 strands of the PpL domain, respectively, with the A strand of the VL domain. PpL is colored light red in both panels. Dashed lines indicate hydrogen-bonded β-strands. D and E, views of the model for an Mub-R5 B1 domain-Fab complex. Mub-R5 is colored blue in both panels. The conserved β2 strand of Mub-R5 makes similar antiparallel hydrogen bonds to PpL to the external VL A-strand (D). However, the polypeptide chain resulting from the insertion of nine amino acids in the loop (colored orange) following β3 in Mub-R5 relative to PpL clashes with the Ig light-chain domain (E) suggesting that a similar parallel hydrogen-bonding interaction with the Fab region may not occur with the mucus-binding protein repeat structure.