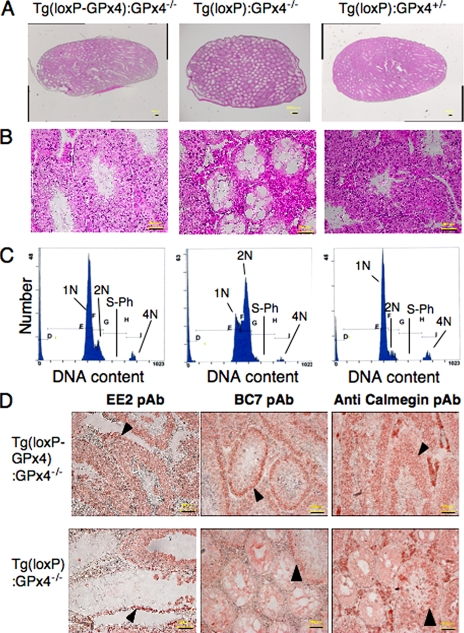
FIGURE 5.
Histopathological observation of testes from spermatocyte-specific GPx4 knock-out mice (Tg(loxP):GPx4−/−). A and B, histological observation of testes. Testis sections from Tg(loxP-GPx4):GPx4−/−, Tg(loxP):GPx4−/−, and Tg(loxP):GPx4+/− mice were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. A, scale bars, 200 μm. B, scale bars, 50 μm. C, analysis of germ cell DNA content in testes from Tg(loxP-GPx4):GPx4−/−, Tg(loxP):GPx4−/−, and Tg(loxP):GPx4+/− mice by flow cytometry. 1N represents haploid cells, 2N represents diploid cells, and 4N represents tetraploid cells. S-phase (S-Ph) represents spermatogonial cells, and preleptotene spermatocytes synthesizing DNA. D, immunohistochemical analysis of the distribution of stage-specific germ cell. Testis sections from Tg(loxP-GPx4):GPx4−/− and Tg(loxP):GPx4−/− mice were stained with EE2 pAb, BC7 pAb, and anti-calmegin pAb to visualize spermatogonia (EE2), early spermatocytes (BC7), and late spermatocytes and spermatids (Calmegin). Arrows indicate the location of spermatogonia, early spermatocytes, and late spermatocytes in each panel. Scale bars, 50 μm.