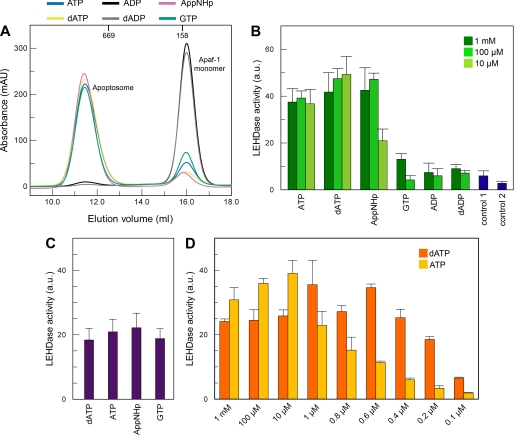
FIGURE 2.
Cofactor requirements for apoptosome formation and caspase-9 activation. A, nucleotide dependence of apoptosome formation. Apaf-1 at a concentration of 10 μm was incubated at 4 °C overnight with a 5-fold excess of cytochrome c and 1 mm nucleotide. The reaction mixtures were analyzed by analytic gel filtration. Apoptosome formation is indicated by strong decrease of the elution volume. Addition of a nucleoside triphosphate (blue, ATP; yellow, dATP; pink, AppNHp; green, GTP) leads to formation of apoptosomes. Incubation with ADP (black curve) or dADP (gray curve) has no effect. The elution volumes of globular marker proteins are indicated. B, nucleotide dependence of caspase-9 activation. Apaf-1 at a concentration of 0.4 μm was incubated at 30 °C for 10 min with 2 μm cytochrome c, 0.2 μm caspase-9, and nucleotide as indicated. Ac-LEHD-AFC was added to a final concentration of 200 μm, and the reaction was fluorometrically monitored. Measurements were done in triplicate; error bars are standard deviations. Control 1 contained no nucleotide; control 2 contained only caspase-9. C, stimulation of caspase-9 activity by the apoptosome is independent of the nucleotide used for assembly. Apoptosomes were assembled using ATP, dATP, AppNHp, and GTP, respectively, and isolated via gel filtration. Isolated apoptosomes equivalent to 0.4 μm Apaf-1 monomer were incubated with 0.2 μm caspase-9 at 30 °C for 10 min. Ac-LEHD-AFC was added to a final concentration of 200 μm, and the reaction was fluorometrically monitored. Measurements were repeated five times; error bars are standard deviations. D, only at very low nucleotide concentrations is dATP more efficient for caspase-9 activation than ATP. Assay conditions are as in B. mAU, milliabsorbance units.